The Complete Guide to the Scrum Workflow – What it is and Benefits of Agile Scrum Workflow

Key takeaways
- The Scrum workflow is an iterative framework that enables teams to develop products efficiently while fostering continuous improvement.
- Workflow Scrum is structured around Sprints, time-boxed iterations that allow teams to plan, develop, and review progress.
- Agile Scrum workflow includes key elements such as Scrum roles, Scrum events, and iterative progress cycles.
- Agile Scrum workflow diagrams provide a visual representation of processes, aiding in workflow transparency and efficiency.
- Sprint retrospective meetings allow teams to evaluate performance, identify improvement areas, and refine future workflows.
- Cflow’s Agile Kanban feature enhances workflow customization, enabling teams to manage tasks more effectively within Scrum frameworks.
What is Scrum Workflow?
Scrum workflow is a structured approach within Agile methodology that organises work into time-boxed iterations called Sprints. It provides teams a framework for managing complex projects, ensuring transparency, accountability, and continuous improvement. By following Scrum principles, teams can prioritise tasks, execute them effectively, and adapt quickly to changes.
In a Scrum workflow, work is divided into small increments completed within a Sprint. Each Sprint follows a cycle that includes planning, execution, review, and retrospective. This iterative approach allows teams to deliver working solutions faster and more efficiently.
The blog will explore the Scrum workflow structure, including Scrum Sprints, Scrum events, Scrum roles, and the responsibilities of a Scrum Master. Additionally, we will discuss the importance of Sprint retrospectives, provide a Scrum workflow diagram, and compare Agile vs. Scrum. Lastly, we will delve into how Cflow’s Agile Kanban feature optimises workflows for better project execution.
Understanding the Scrum Workflow
Scrum workflow follows a systematic approach that enables teams to break down large projects into manageable tasks. It consists of:
Product Backlog
The product backlog is a dynamic list of tasks and features that need to be developed. It is maintained by the Product Owner, who prioritises the items based on business value, customer needs, and technical feasibility. This backlog ensures that teams always have a structured pipeline of tasks to work on, aligning their efforts with organisational goals.
Sprint Planning
Sprint Planning is a collaborative meeting where the Scrum Team selects items from the product backlog to complete during the Sprint. The Product Owner presents the prioritised tasks, and the Development Team estimates the effort required. The goal is to define a clear Sprint backlog, which serves as a roadmap for the upcoming Sprint. Well-executed Sprint planning helps teams set realistic goals and avoid scope creep.
Sprint Execution
Sprint execution is the phase where the development team works on completing the Sprint backlog items. The team collaborates, writes code, tests features, and iterates on improvements. The Scrum Master ensures that team members remain focused, removing any obstacles that hinder progress. Work is carried out in an incremental manner, ensuring that each task contributes towards the Sprint goal.
Daily Scrum Meetings
The Daily Scrum, also known as a Daily Stand-up, is a short, time-boxed meeting (typically 15 minutes) held every day during the Sprint. Team members discuss what they accomplished yesterday, what they plan to do today, and any obstacles they face. These stand-ups promote transparency, foster team communication, and help the Scrum Master identify and address issues promptly.
Sprint Review
At the end of each Sprint, a Sprint Review meeting is conducted where the Scrum Team showcases completed work to stakeholders. This meeting provides an opportunity for feedback, allowing stakeholders to request modifications or suggest improvements. The outcome of the Sprint Review influences the product backlog, ensuring that the next Sprint aligns with business needs.
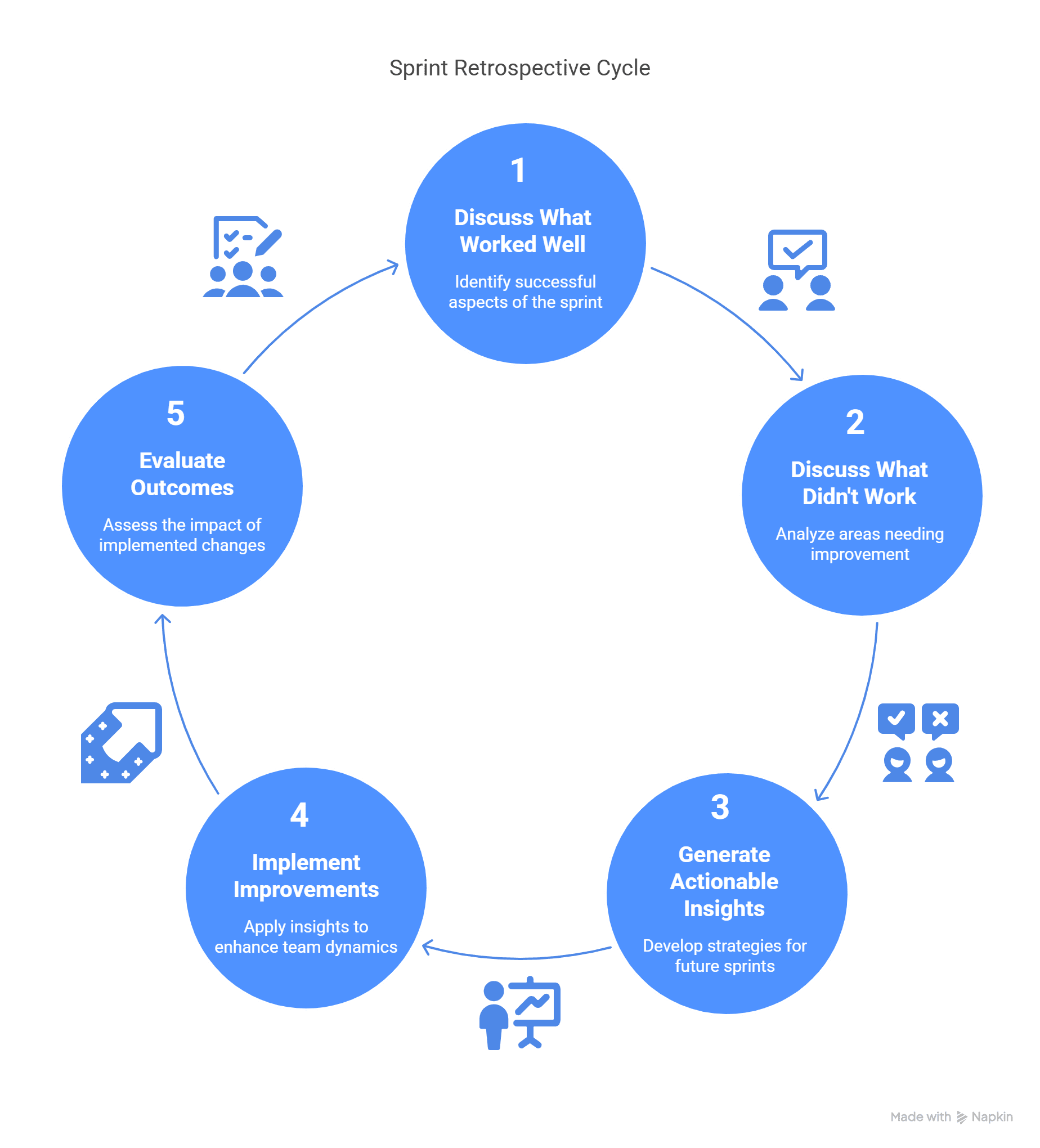
Sprint Retrospective
The Sprint Retrospective is held after the Sprint Review and focuses on process improvement. The team discusses what worked well, what didn’t, and how future Sprints can be optimised. Actionable insights from retrospectives help improve team dynamics, productivity, and efficiency. By continuously iterating on processes, teams ensure that they remain adaptive and efficient in their Scrum workflows.
Each phase ensures a continuous feedback loop, helping teams maintain efficiency, adaptability, and alignment with business objectives.
Speak with our workflow management experts today
What are Scrum Sprints and How to Plan Sprints?
Scrum Sprints are time-boxed iterations, typically lasting 1-4 weeks, where teams focus on completing a set amount of work. Sprints allow teams to deliver working solutions incrementally, ensuring continuous improvement and adaptability to changing requirements.
Each Sprint includes several key events: Sprint Planning, Daily Scrums, Sprint Execution, Sprint Review, and Sprint Retrospective. These structured phases help teams stay focused, manage workloads effectively, and deliver high-quality results within the defined timeframe.
Sprint Planning
Sprint Planning is crucial for defining the goals and tasks to be completed within a Sprint. It is a collaborative session attended by the Product Owner, Scrum Master, and Development Team to establish a shared understanding of what needs to be done and how the team will approach it.
1. Selecting Backlog Items
The team and Product Owner select tasks from the Product Backlog based on priority, ensuring that the highest-value features and improvements are addressed first. The backlog items chosen should align with business goals and customer needs.
2. Defining Sprint Goals
A clear Sprint goal is established to align team efforts. This goal acts as a guiding principle throughout the Sprint, ensuring that all work contributes to a common objective. For example, if the goal is to improve user authentication, the Sprint may include tasks related to security enhancements and user interface improvements.
3. Task Estimation
The team estimates the effort required for each backlog item. Techniques such as Planning Poker, T-shirt Sizing, or Story Points help assign realistic estimates to each task, ensuring that the workload is balanced and achievable within the Sprint duration. Estimating tasks effectively helps prevent burnout and ensures steady progress.
4. Assigning Responsibilities
Developers and stakeholders collaborate to define execution plans and assign tasks based on expertise and workload. This helps in distributing work evenly among team members, ensuring that everyone knows their responsibilities and can work efficiently towards achieving Sprint goals.
5. Creating a Sprint Backlog
Once tasks are selected and assigned, they are documented in a Sprint Backlog, which serves as a dynamic work list for the team. This backlog outlines the scope of the Sprint and provides a clear roadmap for execution.
Proper Sprint planning ensures that the team has a realistic scope, clear objectives, and a structured approach to execution. When done effectively, Sprint planning sets the foundation for a successful Sprint, helping teams maintain efficiency, minimise risks, and deliver high-value work incrementally.
What are Scrum Events?
Scrum workflow includes key events, also known as Scrum ceremonies, that help teams stay aligned, transparent, and focused on continuous improvement. These events structure the workflow and ensure that development stays on track while promoting adaptability to changing requirements.
1. Sprint Planning
Sprint Planning is a collaborative meeting that takes place at the beginning of each Sprint. The Scrum Master, Product Owner, and Development Team participate in this meeting to decide which product backlog items will be worked on during the Sprint.
- Selecting Backlog Items: The team selects high-priority tasks from the Product Backlog based on business goals and customer needs.
- Setting Sprint Goals: A clear objective is defined to ensure team alignment throughout the Sprint.
- Breaking Down Tasks: The team discusses each backlog item and breaks it into smaller, actionable tasks.
- Estimating Workload: Techniques such as Story Points or Planning Poker help assess the effort required for each task.
- Creating the Sprint Backlog: Once tasks are finalised, they are documented in the Sprint Backlog, providing a roadmap for execution.
A well-structured Sprint Planning meeting ensures that the team has a realistic workload and a clear plan for execution.
2. Daily Scrum Meeting
The Daily Scrum, also known as the Daily Stand-up, is a 15-minute time-boxed meeting that occurs every day during the Sprint. It allows the team to track progress, discuss roadblocks, and adjust work priorities if necessary.
- What was accomplished yesterday? Each team member shares what they worked on the previous day.
- What is the plan for today? Members discuss what they will focus on for the current day.
- What obstacles are in the way? Any impediments preventing progress are identified, and the Scrum Master works to resolve them.
This meeting fosters collaboration and transparency, ensuring that the team stays focused and can quickly adapt to challenges.
3. Sprint Review
A Sprint Review is conducted at the end of each Sprint to showcase the completed work to stakeholders. The goal is to gather feedback and determine if the delivered product increments meet business requirements.
- Demonstrating Completed Work: The Development Team presents the work completed during the Sprint.
- Gathering Feedback: Stakeholders provide input on the delivered product, which helps refine future Sprint goals.
- Updating the Product Backlog: Based on feedback, the Product Owner may adjust priorities for upcoming Sprints.
Sprint Reviews ensure that deliverables align with business goals and help teams adapt their approach based on real-time feedback.
4. Sprint Retrospective
A Sprint Retrospective is a reflection meeting held after the Sprint Review. The objective is to analyse team performance and identify opportunities for improvement.
- What went well? The team discusses successes and effective strategies from the Sprint.
- What could be improved? Challenges and roadblocks encountered during the Sprint are addressed.
- Action Plan for Improvement: The team defines specific steps to enhance efficiency in the next Sprint.
By incorporating these Scrum events into their workflow, teams ensure smooth coordination, maintain alignment with business goals, and continuously improve their efficiency and effectiveness.
What is a Sprint Retrospective?
A Sprint Retrospective is a meeting held at the end of a Sprint to discuss what went well, what could be improved, and how to enhance future Sprints.
Sprint Retrospectives foster a culture of continuous learning, helping teams refine their workflows and improve future iterations.
Sprint Retrospective vs. Sprint Review
| Aspect | Sprint Retrospective | Sprint Review |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Evaluate team performance and workflow | Review completed work with stakeholders |
| Participants | Development team | Team + Stakeholders |
| Focus | Process improvement | Product feedback |
| Outcome | Action items for better workflows | Changes to the product backlog |
Benefits of Sprint Retrospective Meetings:
- Enhances Team Collaboration: Encourages open discussion, fostering a team-oriented mindset.
- Identifies Improvement Areas: Helps recognise workflow inefficiencies and implement corrective actions.
- Promotes Continuous Learning: Creates a culture of innovation and adaptation.
- Improves Team Morale: Provides a platform for appreciating team efforts and resolving concerns.
By incorporating these Scrum events into their workflow, teams ensure smooth coordination, maintain alignment with business goals, and continuously improve their efficiency and effectiveness.
What are Scrum Roles?
Scrum defines three core roles that ensure smooth project execution and alignment with Agile principles.
- Product Owner
The Product Owner is responsible for maximising the value of the product by managing the Product Backlog. They act as the liaison between stakeholders and the development team, ensuring that the work aligns with business goals and customer needs. Their responsibilities include:- Defining and prioritising backlog items.
- Communicating business goals and customer expectations to the team.
- Making final decisions on scope and requirements.
- Ensuring that the development effort delivers maximum value.
- Scrum Master
The Scrum Master is responsible for ensuring that Scrum practices are followed and that the team remains productive. They act as facilitators, helping to remove roadblocks and ensuring seamless collaboration between team members. Key responsibilities include:- Facilitating Scrum events such as Sprint Planning, Daily Stand-ups, Sprint Reviews, and Retrospectives.
- Coaching the team on Agile principles and best practices.
- Identifying and eliminating obstacles that hinder team progress.
- Ensuring a collaborative and transparent work environment.
- Development Team
The Development Team consists of professionals responsible for delivering the work defined in the Sprint Backlog. This self-organising team collaborates to design, develop, test, and deploy product increments. Their key responsibilities include:- Breaking down user stories into actionable tasks.
- Estimating effort and completing Sprint tasks efficiently.
- Conducting peer reviews and ensuring code quality.
- Actively participating in Scrum events and providing feedback.
Each role in Scrum is essential to ensuring that projects remain efficient, adaptable, and aligned with business goals.
What is a Scrum Master?
A Scrum Master is responsible for ensuring that Scrum principles are followed and that the team operates efficiently. They act as a servant leader who facilitates Scrum processes, removes obstacles, and ensures that the team is continuously improving. Unlike a traditional project manager, a Scrum Master does not dictate work but instead empowers the team to self-organise and function efficiently within the Agile framework.
Unleash the full potential of your AI-powered Workflow
Key Responsibilities of a Scrum Master
1. Facilitating Scrum Events
The Scrum Master ensures that all Scrum ceremonies—Sprint Planning, Daily Stand-ups, Sprint Review, and Sprint Retrospective—are conducted effectively. They help the team stay on track, clarify goals, and ensure that meetings remain productive. By acting as a facilitator, the Scrum Master helps streamline discussions, keeping them focused and goal-oriented.
2. Removing Obstacles
One of the primary duties of a Scrum Master is identifying and eliminating obstacles that hinder the development team’s progress. This could involve resolving conflicts within the team, addressing technical roadblocks, or ensuring that team members have access to necessary resources. A proactive Scrum Master continuously monitors potential risks and mitigates them before they impact the Sprint.
3. Coaching Team Members on Agile Practices
The Scrum Master plays a crucial role in educating the team about Agile principles and Scrum methodologies. They coach both new and experienced team members on best practices, helping them transition to an Agile mindset. Additionally, they train stakeholders and leadership on Agile processes, ensuring that Scrum is fully integrated into the organisation’s workflow.
4. Ensuring Continuous Improvement
A key function of the Scrum Master is fostering a culture of continuous improvement. By facilitating Sprint Retrospectives, they help the team reflect on their performance, identify areas of improvement, and implement actionable changes. Encouraging feedback loops and experimentation enables the team to enhance efficiency and deliver higher-quality results.
5. Encouraging Collaboration and Transparency
The Scrum Master promotes open communication between team members, ensuring that information flows seamlessly. By fostering an environment of trust and collaboration, they enable team members to work effectively without fear of failure. They also ensure that project progress, challenges, and decisions are visible to all stakeholders through tools such as Scrum boards and burndown charts.
6. Aligning Teams with Business Goals
While Scrum Masters focus on the development team, they also collaborate with Product Owners to align Sprint goals with business objectives. They assist in backlog refinement, ensuring that priorities reflect customer needs and organisational goals. This alignment ensures that the team is working on high-value tasks that contribute to the company’s success.
Transform your AI-powered approvals
Why is the Scrum Master Role Important?
A Scrum Master is essential for maintaining workflow integrity and driving team productivity. They help teams overcome challenges, maintain Agile discipline, and continuously improve. Without a Scrum Master, teams may struggle with inefficiencies, unclear goals, and a lack of accountability.
By acting as a coach, mentor, and facilitator, the Scrum Master ensures that Agile principles are effectively applied, leading to successful project execution and high-performing teams.
What is a Scrum Workflow Diagram?
A Scrum Workflow Diagram is a visual representation of the iterative process followed in Scrum. It outlines the various phases involved in executing a Scrum project, from backlog management to Sprint execution and review. By using this diagram, teams can better understand how Scrum operates, ensuring transparency and efficient workflow management.
Key Components of a Scrum Workflow Diagram
- Product Backlog
- A prioritised list of features, tasks, and improvements maintained by the Product Owner.
- Contains work items that need to be developed in upcoming Sprints.
- Sprint Planning
- The team selects backlog items to include in the Sprint Backlog.
- Tasks are broken down and estimated based on complexity.
- Goals are defined to align work with business objectives.
- Sprint Execution
- The Development Team works on completing the Sprint backlog items.
- Work progresses through iterative cycles, ensuring incremental improvements.
- Daily Scrum (Stand-up Meetings)
- A short meeting (typically 15 minutes) is held every day during the Sprint.
- Helps track progress, identify roadblocks, and realign work priorities.
- Sprint Review
- The team showcases completed work to stakeholders.
- Feedback is gathered, and necessary changes are documented in the backlog.
- Sprint Retrospective
- A reflection meeting to analyse team performance and identify areas of improvement.
- Encourages continuous learning and process refinement.
A Scrum Workflow Diagram simplifies understanding of the Scrum process by providing a structured overview of work progression. It ensures that all team members and stakeholders are aligned, facilitating smooth collaboration and efficient execution.
End-to-end workflow automation
Build fully-customizable, no code process workflows in a jiffy.
Key Differences Between Agile and Scrum
| Feature | Agile | Scrum |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A methodology emphasising iterative development | A framework within Agile for team collaboration |
| Structure | Flexible, broad approach | Structured framework with specific roles and events |
| Focus | Continuous improvement and adaptability | Sprint-based development with defined iterations |
| Roles | Roles vary based on implementation | Defined roles: Scrum Master, Product Owner, and Development Team |
| Meetings | Varies based on methodology | Includes specific Scrum ceremonies like Sprint Planning, Daily Standups, Sprint Review, and Retrospectives |
| Flexibility | Can be adapted to various frameworks like Kanban, Lean, or XP | Follows a structured, rule-based approach |
Benefits of Using Scrum Workflow
1. Increased Productivity
Scrum workflow improves productivity by breaking down work into smaller, manageable tasks. The time-boxed nature of Sprints ensures that teams remain focused on priorities, reducing distractions and inefficiencies.
2. Enhanced Collaboration
Scrum promotes transparency and collaboration between team members, stakeholders, and the Product Owner. Daily stand-ups and Sprint Reviews ensure continuous communication and alignment with project goals.
3. Better Project Visibility
With Scrum boards, burndown charts, and backlog management, teams have a clear view of progress, upcoming tasks, and roadblocks. This visibility helps in making real-time adjustments and ensuring project success.
4. Faster Time-to-Market
By delivering work in iterative cycles, Scrum ensures that products reach users faster. Instead of waiting for the entire project to be completed, Scrum allows teams to release increments at the end of each Sprint.
5. Continuous Improvement
The Sprint Retrospective encourages self-reflection and ongoing improvements. Teams learn from past experiences, refine processes, and optimise workflows to enhance efficiency.
6. Risk Mitigation
Scrum enables early detection of potential risks by maintaining frequent feedback loops. Issues are addressed proactively rather than surfacing at the final stages of development.
7. Customer-Centric Approach
Frequent stakeholder involvement ensures that the end product aligns with customer needs. Scrum allows for adaptability to changing market demands and customer feedback, improving user satisfaction.
8. Higher Product Quality
Scrum’s emphasis on incremental testing and review cycles ensures that defects are identified and resolved early, leading to higher-quality deliverables.
By leveraging the Scrum workflow, organisations can foster agility, adaptability, and efficiency in their development processes, ensuring successful project outcomes and continuous growth.
Unleash the full potential of your AI-powered Workflow
Cflow and Agile Kanban
Cflow enhances Agile workflows through its Kanban feature, allowing teams to:
- Visualise work progress with drag-and-drop functionality.
- Customise workflows based on Agile methodologies.
- Optimise task allocation and efficiency through automation.
- Enhance Sprint tracking with real-time updates.
Cflow’s Agile Kanban Feature ensures streamlined project execution.
Conclusion
Scrum workflow empowers teams to work efficiently, deliver high-quality results, and continuously improve. By incorporating Scrum principles, businesses can achieve greater agility and scalability in project execution.
Cflow’s automation features further enhance Agile and Scrum processes, ensuring smoother workflows and better project visibility. Try Cflow today to streamline your Scrum workflow and maximise productivity.
Discover why teams choose Cflow
FAQs
What is Scrum Workflow?
Scrum workflow is a structured Agile framework that organises work into iterative Sprints to ensure efficiency and collaboration.
How does Scrum differ from traditional project management?
Scrum emphasises flexibility, collaboration, and iterative progress, unlike traditional linear project management approaches.
What are the benefits of a Sprint Retrospective?
It helps teams reflect on performance, identify bottlenecks, and improve future Sprints.
What are the key Scrum roles?
Scrum defines three main roles: Product Owner, Scrum Master, and Development Team.
How can Cflow support Scrum workflows?
Cflow’s Agile Kanban feature enhances task visualisation, automation, and real-time tracking to optimise Scrum execution.
Related Articles:
- A Complete Guide to Understanding Agile Workflows
- Best Agile Process Management Software for Teams
- Learn How to Prioritise Tasks in 10 Easy Techniques
- 10 Most Effective Issue Tracking Software Tools in 2025
- 10 Workflow Apps for Process Management in 2025
Thanks for reading till the end. Here are 3 ways we can help you automate your business: Create workflows with multiple steps, parallel reviewals. auto approvals, public forms,
etc. to save time and cost. Get a 30-min. free consultation with our Workflow expert to optimize
your daily tasks. Explore our workflow automation blogs, ebooks, and other resources to master
workflow automation.What should you do next?

Do better workflow automation with Cflow

Talk to a workflow expert

Get smarter with our workflow resources
Get Your Workflows Automated for Free!
Modern software development requires speed, efficiency, and agility to stay competitive. Companies that still rely on traditional software development models often struggle with long development cycles, siloed teams, and inefficient deployments. This is where DevOps workflow comes into play.
A DevOps workflow automates and streamlines the software development, integration, testing, and deployment processes, allowing development and operations teams to collaborate seamlessly. By eliminating manual bottlenecks and integrating CI/CD pipelines, automated testing, and infrastructure as code (IaC), DevOps accelerates product delivery without compromising stability.
According to Puppet’s State of DevOps Report, high-performing DevOps teams deploy 200 times more frequently and recover from failures 24 times faster than non-DevOps teams. The ability to respond quickly to customer demands, security vulnerabilities, and market trends makes DevOps a game-changer for businesses.
In this guide, we’ll explore the DevOps workflow and its benefits, key phases, challenges, and best practices to help organizations implement a robust strategy.
What Is a DevOps Workflow?
A DevOps workflow is a structured framework that integrates software development (Dev) and IT operations (Ops) to streamline the software delivery lifecycle. It emphasises automation, collaboration, and continuous feedback to enhance efficiency, minimise errors, and accelerate releases. DevOps workflows break down traditional silos between teams, ensuring that code development, testing, deployment, and monitoring happen in a seamless, iterative manner.
By leveraging CI/CD pipelines, automation tools, and real-time monitoring, businesses can improve software reliability, security, and scalability. This approach ensures that new features, bug fixes, and updates are delivered rapidly while maintaining high-quality software performance.
How Does a DevOps Workflow Work?
A DevOps workflow consists of six key phases, ensuring continuous software development, testing, and deployment with minimal human intervention.
1. Continuous Development
This phase involves frequent updates to the codebase. Developers write and commit code changes in small, manageable increments rather than in large releases. Version control systems like GitHub, GitLab, or Bitbucket help track changes efficiently. This iterative approach enables rapid innovation, early issue detection, and easier rollback if necessary.
2. Continuous Integration (CI)
In this phase, developers merge their code changes frequently into a shared repository. Each update is automatically built and tested using CI tools like Jenkins, CircleCI, or GitLab CI/CD. This ensures that new code integrates smoothly with the existing codebase, preventing compatibility issues and reducing deployment risks.
3. Continuous Testing
Automated testing plays a critical role in DevOps. Tools like Selenium, JUnit, and TestNG execute unit, integration, and performance tests to validate the stability of new code. Running automated tests throughout the pipeline ensures that defects are identified early in the development process, reducing debugging efforts post-deployment.
4. Continuous Monitoring & Feedback
Once software is deployed, real-time monitoring tools like Prometheus, Datadog, and New Relic provide insights into system performance, security vulnerabilities, and potential failures. Logging and alerting systems send instant notifications to DevOps teams, allowing them to proactively fix issues before they impact users.
5. Continuous Deployment (CD)
After passing all quality checks, new features or updates are automatically deployed to the production environment. Tools like Docker, Kubernetes, and Ansible facilitate containerised deployments and infrastructure as code (IaC), ensuring a scalable and reliable application environment. This minimises manual intervention, speeds up software delivery, and eliminates bottlenecks.
6. Continuous Operations
This phase ensures that deployed applications remain high-performing, secure, and scalable. IT teams use automated incident management, security patching, and infrastructure monitoring to maintain system stability. Regular post-deployment reviews and feedback loops enable businesses to make ongoing improvements, ensuring long-term software reliability.
What Are the Benefits of a DevOps Workflow?
deployment, ensuring faster releases, higher efficiency, and improved collaboration between teams. By eliminating bottlenecks and enhancing agility, organisations can deliver better software solutions while optimising costs. Below are some key benefits of adopting a DevOps workflow –
1. More Effective Collaboration
DevOps eliminates silos between development and operations teams, promoting seamless communication and shared responsibility. This leads to faster problem resolution, better coordination, and higher productivity. By fostering cross-functional teamwork, organisations can deliver software faster with fewer errors.
2. Reduced Costs
By automating manual workflows, organisations reduce labour costs and operational expenses. DevOps minimises downtime, rework, and debugging efforts, leading to long-term financial savings. Cloud-based DevOps solutions also optimise infrastructure costs, ensuring businesses only pay for what they use.
3. Improved Product Quality
Continuous integration and testing ensure that software is frequently tested for errors and vulnerabilities before release. DevOps practices catch defects early, reducing post-deployment failures and ensuring a more stable, high-performing product. This leads to better customer satisfaction and fewer production issues.
4. Technical Scalability
DevOps makes it easier to scale applications and infrastructure by using automation tools such as Kubernetes, Terraform, and AWS Auto Scaling. Businesses can handle increased user demand, optimise cloud resources, and ensure high availability without excessive manual intervention.
5. Better Customer Experience
Frequent software updates and faster bug resolution result in improved user experience and higher retention rates. By continuously monitoring application performance, businesses can deliver seamless experiences with fewer disruptions, keeping customers engaged and satisfied.
6. Promotes Agility
A DevOps approach enhances agility by allowing teams to respond quickly to market demands, security threats, and evolving business needs. Automated pipelines ensure faster feature rollouts, giving businesses a competitive advantage in software innovation.
7. Encourages Business Innovation
By automating repetitive tasks, DevOps allows teams to focus on creative problem-solving and innovation. Businesses can experiment with new technologies, optimise product features, and scale digital transformation efforts without being burdened by inefficient workflows.
Discover why teams choose Cflow
Six Phases of a DevOps Workflow
A successful DevOps workflow consists of six continuous phases that ensure seamless software development, deployment, and maintenance. Each phase is automated and optimised to maximise efficiency and minimise downtime.
1. Continuous Development
Developers write and commit small, incremental code changes frequently rather than in large batches. Version control tools like Git, GitHub, and Bitbucket help track changes, roll back errors, and maintain a structured development process.
2. Continuous Integration (CI)
In this phase, automated pipelines compile, test, and merge new code into a shared repository multiple times daily. CI tools such as Jenkins, Travis CI, and CircleCI help detect bugs early in the development process, reducing integration failures.
3. Continuous Testing
Automated testing ensures that new code changes are stable and reliable before deployment. Testing frameworks such as Selenium, JUnit, and TestNG run unit, integration, and security tests, identifying issues before they impact end users.
4. Continuous Monitoring & Feedback
Using real-time monitoring tools like Prometheus, Splunk, and Datadog, DevOps teams can track system performance, detect anomalies, and proactively fix security vulnerabilities. Continuous feedback ensures that issues are resolved before they escalate into major disruptions.
5. Continuous Deployment (CD)
Once testing is complete, the approved code is automatically deployed to staging or production environments. Tools like Kubernetes, Docker, and Ansible facilitate fast, reliable deployments, eliminating the need for manual interventions.
6. Continuous Operations
This phase ensures that the software remains secure, scalable, and high-performing after deployment. Infrastructure automation tools like Terraform and AWS CloudFormation optimise resource allocation, patch security vulnerabilities, and prevent downtime.
Challenges of Implementing the DevOps Workflow
While DevOps offers numerous benefits, organisations often struggle with adoption due to cultural resistance, technical hurdles, and integration challenges. Below are the primary challenges businesses face when implementing a DevOps workflow –
1. Cultural Change
Shifting from traditional IT silos to a collaborative DevOps culture requires a mindset change. Teams must embrace shared responsibility, transparency, and accountability. Without leadership support and proper training, employees may resist the transition.
2. Technical Challenges
Implementing DevOps requires advanced technical expertise in cloud computing, infrastructure automation, and CI/CD pipelines. Businesses must invest in upskilling employees or hire specialists who understand automation, security, and DevOps best practices.
3. Resistance to Change
Some teams fear job displacement due to automation, while others hesitate to adopt new tools. Overcoming this challenge requires clear communication, hands-on training, and an incremental DevOps adoption strategy to ensure smooth transitions.
How to Create a DevOps Workflow Strategy
Developing a successful DevOps workflow strategy requires careful planning, goal setting, and continuous refinement. A structured approach ensures seamless software development, deployment, and monitoring while eliminating inefficiencies. Below are the essential steps to establish an effective DevOps workflow –
1. Assess Your Current Processes
Begin by evaluating your existing software development and deployment pipelines to identify bottlenecks, redundancies, and areas needing automation. Conduct a gap analysis to understand where manual efforts slow down the process and how DevOps practices can enhance efficiency.
2. Define Clear Goals
Establish measurable DevOps objectives, such as faster release cycles, improved security compliance, increased deployment frequency, and enhanced infrastructure resilience. Align these goals with business objectives to ensure that DevOps implementation drives meaningful outcomes.
3. Choose the Right DevOps Tools
Select tools that match your DevOps requirements. Use Jenkins for CI/CD automation, Terraform for infrastructure as code (IaC), Kubernetes for container orchestration, and Ansible for configuration management. Ensure these tools integrate seamlessly with your existing tech stack.
4. Automate Wherever Possible
DevOps thrives on automation. Automate code integration, testing, deployment, infrastructure provisioning, and monitoring using tools like Docker, Chef, and GitLab CI/CD. This reduces manual errors, accelerates delivery, and improves system stability.
5. Implement Continuous Testing & Feedback
Adopt automated testing frameworks like Selenium, JUnit, and Postman to detect issues early. Establish feedback loops to continuously collect input from developers, operations teams, and end users, ensuring continuous improvement.
6. Measure & Optimise
Track critical DevOps KPIs such as deployment success rates, MTTR (Mean Time to Repair), error resolution time, software performance metrics, and cost savings from automation. Continuously refine the DevOps strategy based on data-driven insights and evolving business needs.
End-to-end workflow automation
Build fully-customizable, no code process workflows in a jiffy.
Streamline Your DevOps Processes with Cflow
Cflow is a no-code workflow automation platform that simplifies DevOps processes by automating approvals, tracking deployments, and enhancing collaboration between development and operations teams. By eliminating manual bottlenecks, Cflow enables businesses to achieve faster, more reliable software releases while ensuring compliance and security.
How Cflow Enhances DevOps Workflow Efficiency –
- Automated Workflow Approvals – Streamlines code deployment, change management, and issue tracking through an intuitive approval system, reducing delays in the development cycle.
- Seamless Tool Integrations – Connects with GitHub, Jenkins, Docker, Kubernetes, AWS, and other DevOps tools, ensuring smooth execution across the software lifecycle.
- Real-Time Monitoring & Notifications – Provides instant alerts, log tracking, and performance insights to optimise system health, detect failures early, and reduce downtime.
- Customizable DevOps Pipelines – Enables teams to create tailored workflows for software development, deployment, and monitoring, enhancing efficiency and automation.
- Scalable & Secure Solutions – Ensures compliance with industry standards, data protection protocols, and seamless scalability, making it ideal for enterprise-level DevOps environments.
With Cflow, businesses can automate complex DevOps workflows, increase collaboration, and improve deployment speed, ultimately enhancing operational agility and software reliability.
Final Thoughts
A well-structured DevOps workflow is critical for accelerating development cycles, improving software quality, and driving business agility. Organisations that embrace DevOps processes benefit from automated deployments, real-time monitoring, and seamless team collaboration, leading to faster issue resolution, enhanced security, and reduced operational costs. With a robust DevOps strategy, businesses can enhance customer experience, minimise downtime, and stay ahead in today’s fast-paced digital landscape.
To streamline your DevOps workflow, sign up and leverage Cflow’s automation platform and experience faster, more efficient development cycles. Get started today!
FAQs
1. What is a DevOps workflow, and how does it improve software development?
A DevOps workflow is a structured approach that integrates development (Dev) and IT operations (Ops) to enable continuous development, testing, deployment, and monitoring. Automating key processes and fostering collaboration reduces manual errors, enhances product quality, and accelerates release cycles.
2. How does automation enhance the DevOps process?
Automation in DevOps workflows eliminates repetitive tasks such as code integration, testing, deployment, and monitoring, ensuring faster and more efficient software delivery. It reduces human intervention, minimises errors, and improves overall workflow consistency.
3. What are the key factors to consider when implementing a DevOps workflow?
When setting up a DevOps workflow, businesses should focus on automation, collaboration, and continuous improvement. Key considerations include:
- Choosing the right DevOps tools (GitHub, Jenkins, Kubernetes, Terraform).
- Implementing CI/CD pipelines for seamless integration and deployment.
- Ensuring robust monitoring and security to detect vulnerabilities.
- Encouraging cross-functional collaboration between development, IT, and security teams.
- Establishing feedback loops for continuous optimisation and performance tracking.
Thanks for reading till the end. Here are 3 ways we can help you automate your business: Create workflows with multiple steps, parallel reviewals. auto approvals, public forms,
etc. to save time and cost. Get a 30-min. free consultation with our Workflow expert to optimize
your daily tasks. Explore our workflow automation blogs, ebooks, and other resources to master
workflow automation.What should you do next?

Do better workflow automation with Cflow

Talk to a workflow expert

Get smarter with our workflow resources
Get Your Workflows Automated for Free!