How to Streamline the Product Part Approval Process in Manufacturing

Key takeaways
- Digitising the Product Part Approval Process (PPAP) eliminates manual errors and speeds up supplier part validation in manufacturing.
- Streamlined PPAP workflows improve compliance with IATF 16949, ISO 9001, and customer-specific standards.
- Centralised document control ensures accurate versioning, traceability, and audit-readiness across engineering, quality, and procurement teams.
- No-code workflow automation tools like Cflow simplify routing, approvals, and document management within the PPAP lifecycle.
Product Part Approval Process (PPAP) plays a pivotal role in ensuring that supplied parts meet customer specifications before mass production begins. However, many manufacturers still rely on spreadsheets, email threads, or legacy systems to manage PPAP workflows—resulting in missed deadlines, approval delays, and audit issues.
How to streamline the product part approval process in manufacturing is a pressing concern for companies looking to improve compliance, reduce costs, and accelerate product launch cycles. Whether you are a supplier, OEM, or quality manager, digitising and automating PPAP can be a game-changer.
This blog explores what PPAP entails, the challenges of the traditional process, and actionable strategies to streamline it using modern workflow solutions.
What is the Product Part Approval Process (PPAP)?
The Production Part Approval Process (PPAP) is a quality assurance protocol used in manufacturing to ensure that components produced by a supplier consistently meet the customer’s engineering and quality requirements—not just once, but throughout mass production. Defined by the Automotive Industry Action Group (AIAG), PPAP plays a central role in manufacturing environments where precision, repeatability, and compliance are essential.
Though PPAP was originally created for the automotive industry, its rigorous standards are now widely adopted across manufacturing sectors such as aerospace, industrial equipment, electronics, and heavy machinery. In these industries, even a minor deviation in part quality can cause major disruptions, product recalls, or regulatory penalties. PPAP helps manufacturers avoid these risks by validating the entire production process—from design intent to shop floor execution.
At its core, PPAP serves as a gatekeeping process before full-scale production begins. It requires suppliers to demonstrate, through documentation and sample parts, that:
- The manufacturing process is stable and under control.
- The part meets all dimensional, material, and performance specifications.
- All quality risks have been identified and addressed in advance.
The process consists of 18 standard elements, each providing evidence of process capability and product conformity. For manufacturers, these elements represent a systematic checklist that ensures every stage of production is accounted for:
- Design Records confirm alignment with customer blueprints and specifications.
- Process Flow Diagrams map each step of the manufacturing workflow, including tooling, handling, and inspections.
- Control Plans define how each critical feature of the part is monitored and controlled on the shop floor.
- Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) anticipates where defects could occur in the process and outlines mitigation strategies.
- Measurement System Analysis (MSA) ensures that inspection equipment used on the line is precise and reliable.
- Initial Sample Inspection Reports (ISIR) validate that the first production parts meet the defined tolerances.
- Part Submission Warrant (PSW) summarises the submission package and declares that all customer requirements are met.
Manufacturers are often required to submit these elements according to one of five PPAP levels, depending on the risk level of the part and customer requirements:
- Level 1: PSW only
- Level 2: PSW + selected supporting data
- Level 3: PSW + full supporting data (most common in manufacturing)
- Level 4: PSW + data as defined by the customer
- Level 5: PSW + full data reviewed at the supplier’s site
Among these, Level 3 PPAP is the most widely used in manufacturing due to its balance of rigour and practicality. It requires a complete submission including all documentation and sample parts, allowing both supplier and customer to validate tooling, processes, and inspection routines before approving mass production.
In modern manufacturing, PPAP is not just a compliance exercise—it’s a foundation for operational excellence. It drives standardisation, strengthens supplier relationships, and ensures parts are production-ready with minimal rework or deviation. Manufacturers that implement PPAP effectively gain a competitive advantage by reducing quality costs, accelerating time to market, and reinforcing customer trust.
Why Streamlining PPAP Matters in Manufacturing
In high-stakes manufacturing industries—such as automotive, aerospace, electronics, and heavy machinery—product reliability and regulatory compliance are non-negotiable. A single non-conforming part can trigger a cascade of operational and reputational consequences. From production halts to product recalls, the impact of a flawed part reverberates across the supply chain, leading to financial losses and customer dissatisfaction.
Some of the most critical risks manufacturers face due to inefficient or incomplete PPAP processes include:
- Product Recalls: Faulty or unverified parts can compromise performance or safety, often resulting in large-scale recalls that damage brand reputation and erode customer trust.
- Regulatory Penalties: Failure to meet standards like IATF 16949 or ISO 9001 can lead to failed audits, penalties, or even lost business, particularly in regulated sectors.
- Customer Dissatisfaction: Late submissions, documentation gaps, or quality inconsistencies can break customer confidence and lead to strained relationships or lost contracts.
- Production Downtime: If PPAP approval is delayed, production lines may sit idle waiting for parts, disrupting schedules and increasing operational costs.
Key Advantages of Streamlining PPAP Workflows in Manufacturing
Streamlining PPAP workflows through digital automation not only eliminates inefficiencies but also strengthens process control, collaboration, and compliance. Below are the key advantages manufacturers can gain by digitising and standardising their PPAP approach:
1. Accelerate Time-to-Market
By automating PPAP submissions and approvals, manufacturers eliminate delays caused by emails, manual signatures, and lost documents. Digital workflows allow simultaneous completion of required elements—like FMEAs and control plans—speeding up validation and reducing time to launch.
2. Ensure End-to-End Traceability
Digital PPAP systems log every document submission, approval, and revision with timestamps. This provides a reliable audit trail for internal reviews and external audits, and ensures that only the most current documentation is used in production.
3. Enhance Cross-Functional Collaboration
PPAP involves multiple departments—engineering, quality, procurement, and suppliers. A centralised digital workflow improves visibility and coordination, allowing all stakeholders to access real-time updates, resolve issues early, and maintain alignment across teams.
4. Improve Compliance with Industry Standards
Streamlined PPAP workflows help manufacturers meet rigorous standards like IATF 16949 and ISO 9001 by ensuring accurate documentation, validated processes, and complete quality records—reducing the risk of audit failures and customer rejections.
5. Reduce Risk of Production Downtime
Manual PPAP processes often lead to approval bottlenecks that delay production. Streamlined workflows ensure that all documents and sample approvals are completed on time, minimising the chances of stalled manufacturing lines and costly idle time.
6. Strengthen Supplier Accountability
A digital PPAP system provides greater visibility into supplier submissions and timelines. By automating reminders and approval checkpoints, manufacturers can hold suppliers accountable for compliance and timeliness, improving overall supply chain reliability.
Challenges in Managing the PPAP Process
Despite its importance, many manufacturers struggle with PPAP due to outdated systems and fragmented workflows.
1. Manual Documentation Errors
Using spreadsheets or Word docs increases the risk of versioning conflicts, missing files, or incorrect data entry.
2. Lack of Real-Time Visibility
When files are shared via email, it’s difficult to track the approval status or know where bottlenecks exist.
3. Delayed Approvals
Without automated routing, documents often sit idle in inboxes, delaying the entire project timeline.
4. Compliance Gaps
Maintaining audit-ready documentation is hard without centralised version control or access logs.
5. Disconnected Systems
Lack of integration with ERP or PLM systems causes duplication of efforts and inconsistencies in part data.
These bottlenecks not only increase risk but also slow down supplier onboarding and new product introduction.
How to Streamline the Product Part Approval Process
To overcome inefficiencies, organisations must transition from manual PPAP handling to digital, workflow-driven solutions. Here are effective strategies to streamline the process:
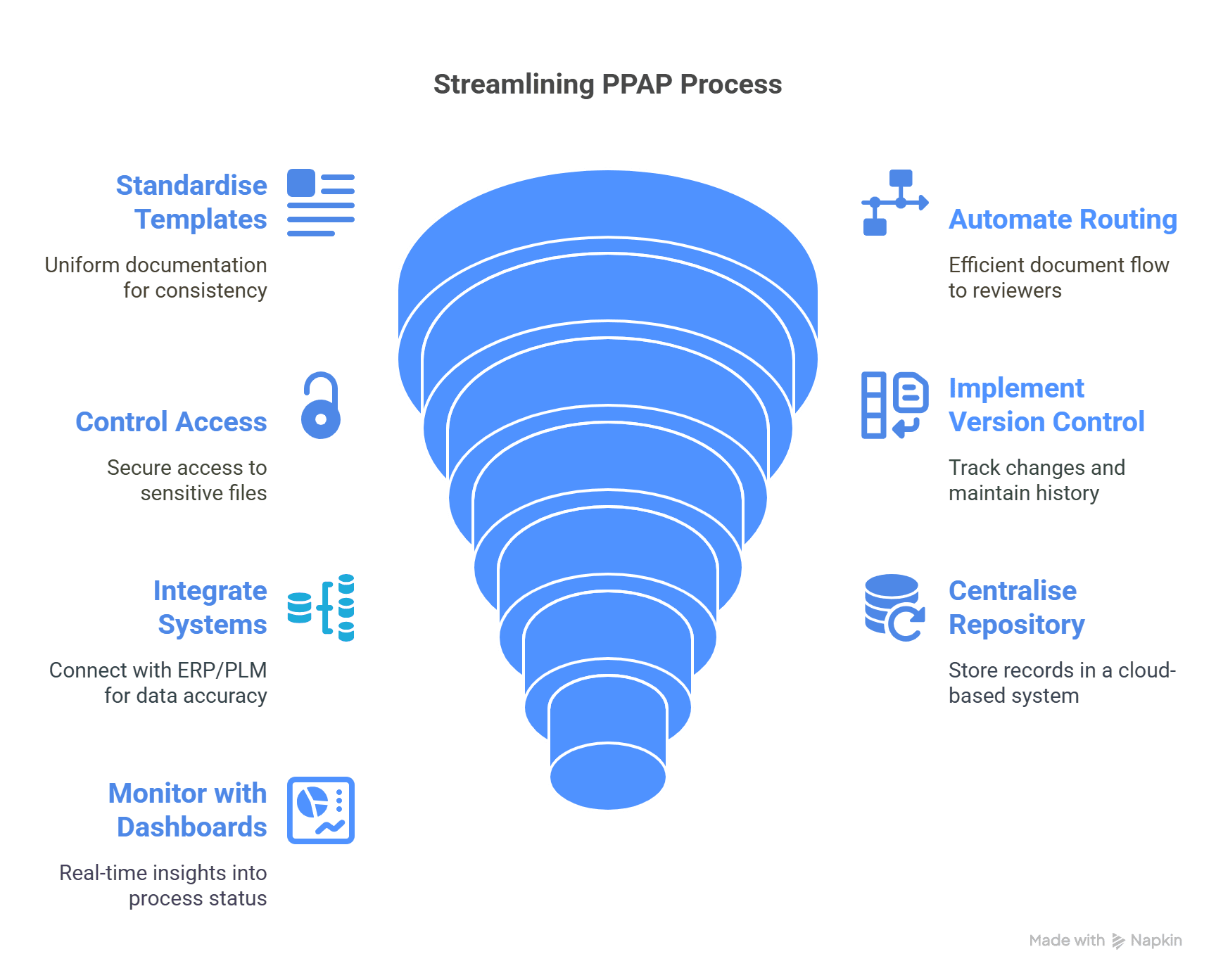
1. Standardise Submission Templates
Use uniform templates for control plans, FMEAs, and other PPAP elements. This reduces back-and-forth and ensures suppliers meet documentation expectations.
2. Automate Document Routing
Use workflow automation tools to assign documents to reviewers based on roles. Auto-notifications and reminders keep the process moving.
3. Enable Role-Based Access Control
Secure sensitive PPAP files by controlling who can upload, approve, or modify documents. This is critical for audit compliance.
4. Implement Version Control
Track changes to each document with time-stamped logs. Maintain a digital history of approvals, edits, and rejections.
5. Integrate with ERP/PLM Systems
Pull part numbers, supplier codes, and BOMs directly into the PPAP system to eliminate data duplication.
6. Maintain a Central Repository
Ensure all PPAP records are stored in a searchable, cloud-based repository. This supports audits and internal reviews.
7. Use Dashboards for Real-Time Monitoring
Gain real-time insights into approval status, pending actions, and upcoming deadlines through dashboards.
Competitive Advantage of a Digitised PPAP
Implementing a model-based approach to PPAP can reduce report generation errors by up to 77%, leading to faster time-to-market and improved quality assurance.
Digitising the Production Part Approval Process (PPAP) transforms it from a compliance exercise into a strategic enabler.
Faster Approval Cycles through Automation
Automated PPAP workflows drastically reduce the back-and-forth between teams. By using digital platforms that support real-time tracking, auto-routing, and escalation alerts, manufacturers can cut down approval times from weeks to days—accelerating time-to-market.
Built-in Audit-Readiness
Digital PPAP tools ensure every document is version-controlled, timestamped, and securely archived. Whether it’s a customer audit or a regulatory inspection, data can be retrieved instantly with a full revision history—eliminating audit-related anxiety.
Improved Cross-Functional Collaboration
Engineering, quality, procurement, and suppliers can collaborate on a unified platform. Role-based access and shared dashboards keep everyone aligned, reducing miscommunication and minimising redundant work.
Becoming the Preferred Supplier
OEMs favour suppliers who are consistent, fast, and audit-ready. Digitised PPAP gives you that edge, turning your operations into a benchmark for quality and reliability.
Supplier Onboarding and Training Strategies
A well-executed PPAP process starts with informed and trained suppliers. Here’s how manufacturers can elevate supplier performance.
Provide Submission Guides and Templates
Create a comprehensive submission manual that walks suppliers through each PPAP element—like Design Records, Control Plans, and Measurement System Analysis. Include sample templates to minimise ambiguity.
Conduct Regular Training and Webinars
Interactive sessions help suppliers stay updated on documentation requirements. Host quarterly webinars or on-demand tutorials to explain common errors and walk through recent changes in standards.
Enable Feedback Loops
Instead of rejecting submissions without explanation, offer annotated feedback. This helps suppliers learn from mistakes, fostering continuous improvement and accountability.
Share Examples of Approved Submissions
A repository of validated PPAP documents serves as a practical reference. When suppliers know what “right” looks like, they’re more likely to meet expectations on the first try.
Why It Matters
Educated suppliers contribute fewer errors, faster turnaround times, and better compliance—making your supply chain more resilient and cost-efficient.
Cost of Non-Compliance: A Quantitative Perspective
The average cost of non-compliance for organisations is approximately $14.82 million, nearly three times higher than the average cost of compliance, which stands at $5.47 million.
Failing to comply with PPAP standards can cost your company more than just rework—it can affect brand reputation and market share.
Delays in Product Launches
Without timely PPAP approvals, production lines remain idle. Each day of delay can lead to thousands in lost revenue, especially in high-volume manufacturing settings.
Expensive Rework and Recalls
Unverified parts pose safety and performance risks. A single defective component can trigger recalls, legal issues, or warranty claims that cost millions—particularly in regulated industries like automotive or aerospace.
Audit Penalties and Supplier Status Risks
Non-compliance during a client or third-party audit can result in penalties, blacklisting, or removal from preferred supplier lists. Recovery from such reputational damage is often slow and costly.
The Real Cost of Poor Quality
Industry research suggests poor quality and compliance issues can amount to 12–15% of total operational costs. These aren’t just quality control failures—they’re financial liabilities.
A Financially Sound Investment
Automating PPAP not only improves documentation quality but also prevents revenue leaks—making it a smart business move.
Future of PPAP: AI, Predictive Analytics, and Smart Manufacturing
The next evolution of PPAP aligns with the principles of Industry 4.0, where intelligence and automation drive continuous improvement.
AI-Driven Document Validation
AI tools are now capable of reviewing PPAP submissions for common mistakes—such as missing entries or mismatched specifications—before they reach human reviewers. This proactive validation saves time and reduces rework.
Predictive Risk Scoring
By analysing historical PPAP data, predictive analytics can identify high-risk parts, suppliers, or process bottlenecks. This helps prioritise approvals and allocate resources strategically.
Integration with IoT and MES
Smart factories will soon integrate PPAP systems with Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) and IoT sensors. For instance, if a sensor detects a deviation on the shop floor, it can trigger a compliance workflow linked to PPAP elements in real time.
From Static to Dynamic Compliance
Instead of treating PPAP as a one-time submission process, manufacturers can use it as a living quality system—updated automatically based on production feedback, supplier input, and customer changes.
Intelligent, Autonomous PPAP
The future PPAP process will be self-regulating, with minimal human intervention. Approvals, alerts, and compliance checks will be handled by AI, creating a seamless bridge between product design, supplier input, and shop-floor execution.
Real-World Use Cases of PPAP Implementation
Leading manufacturers implement structured PPAP processes to ensure supplier quality and compliance. Below are verified examples of how major companies manage and support PPAP in their operations.
1. Ford Motor Company’s Phased PPAP Workflow
Ford Motor Company has long prioritised part quality and compliance, especially when launching new engine components from Tier 1 suppliers. To streamline their Production Part Approval Process (PPAP) across global operations, Ford introduced a Global Phased PPAP approach. This system mandates structured submission levels—such as Levels 1, 3, and 5—based on the criticality of the part.
Suppliers submit required documents like control plans and PSWs through a centralised digital portal, which automatically routes submissions to engineering and quality teams. This approach significantly reduces email-based back-and-forth and enables faster turnaround. As a result, Ford has been able to validate safety-critical parts within 48 hours, accelerating time-to-market while ensuring strict adherence to IATF 16949 standards.
2. Bosch Streamlines PPAP with SAP Integration
Bosch, a global leader in automotive and industrial technology, faced challenges managing supplier documentation and quality workflows across divisions. Manual PPAP tracking led to delays in part approvals and inconsistencies in documentation control. To address this, Bosch integrated its PPAP workflows into the SAP Service Cloud and SAP ERP platforms.
This integration allowed supplier submissions to be tracked in real time, with automated routing to relevant departments for review and approval. It also enabled a single source of truth for logistics, order status, and quality records. The move not only improved collaboration across supply chain and quality teams but also ensured that all submissions complied with both internal and customer-specific standards. This digital infrastructure enhanced audit readiness and significantly reduced part validation timelines.
3. Cummins India Digitises PPAP with Siemens Teamcenter
Cummins India, a subsidiary of the global power technology company, encountered bottlenecks in its PPAP process due to manual form submissions and fragmented communication between engineering and supplier teams. In response, Cummins adopted Siemens Teamcenter, a PLM platform that digitised and standardised PPAP submissions.
Elements like DFMEA, PFMEA, control plans, and PSW were transformed into structured digital templates, ensuring completeness and consistency. Teamcenter’s built-in dashboards enabled teams to track submission status and document versions in real time. By automating approvals and centralising document control, Cummins reduced average PPAP cycle times by 30% and improved first-time submission accuracy by 40%. The platform also enhanced audit trail integrity and compliance with OEM requirements.
End-to-end workflow automation
Build fully-customizable, no code process workflows in a jiffy.
Features to Look for in a PPAP Workflow Solution
Selecting the right platform to digitise the Production Part Approval Process (PPAP) can dramatically impact compliance, efficiency, and supplier collaboration. When evaluating PPAP workflow solutions, businesses should prioritise a robust set of features designed to eliminate manual inefficiencies and ensure audit readiness.
1. Customizable workflows and templates are essential for aligning the PPAP process with your organisation’s specific documentation structure and approval stages. The ability to tailor forms for FMEAs, control plans, and PSWs ensures consistency and accuracy across submissions.
2. Automated notifications and escalations keep the process on track by sending timely alerts to approvers and escalating overdue tasks. This ensures that submissions don’t get stuck in review cycles, reducing delays in part approvals.
3. ERP and PLM integration capabilities allow the workflow solution to pull real-time data—such as part numbers, supplier details, and bill of materials—directly from systems like SAP, Oracle, or Teamcenter. This eliminates duplicate data entry and aligns PPAP documents with current production data.
4. Full audit trails provide a clear record of who reviewed, approved, or modified each document. This is critical for internal quality checks and for demonstrating compliance during external audits.
5. Compliance checklists help ensure that submissions meet the requirements of standards like IATF 16949, AS9100, and ISO 9001. Built-in validation rules and reference templates reduce the risk of missing or incomplete documentation.
6. A secure cloud-based repository centralises all PPAP documentation, making it easy to retrieve records during audits or customer reviews. It also facilitates collaboration across global supplier networks.
Lastly, analytics dashboards offer real-time insights into submission timelines, bottlenecks, and approval trends. Managers can use this data to improve process efficiency and supplier performance.
Tools like Cflow offer all these features in a no-code environment, enabling quality and procurement teams to build and manage PPAP workflows without needing IT intervention. This accessibility makes it easier to scale standardised, compliant workflows across the organisation.
The ROI of Streamlining PPAP
Digitising and automating the PPAP process isn’t just about operational convenience—it has a measurable business impact. A streamlined PPAP system leads to faster part approvals, typically reducing turnaround times by 20–30%. With digital routing and pre-validated templates, approval cycles are shortened, helping projects stay on track.
Automation also results in a 50% reduction in rejected submissions, as real-time validations, standardised formats, and checklist-driven forms ensure completeness and accuracy from the outset. This reduction in rework boosts team productivity and reduces supplier frustration.
Streamlined PPAP workflows contribute to stronger supplier relationships by providing clarity, transparency, and predictable review timelines. Suppliers are more likely to meet quality expectations when they have access to consistent submission guidelines and feedback loops.
From a compliance standpoint, automated workflows make it easier to align with IATF 16949, AS9100, and ISO 9001 standards. Built-in controls, role-based access, and audit trails reduce the risk of non-conformance during quality audits.
Moreover, faster approvals and fewer errors mean shorter production timelines and quicker market entry. For industries with high product development costs or competitive launch windows—such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics—this translates into real business value.
In essence, investing in a digital PPAP solution reduces operational costs, eliminates bottlenecks, and enhances product quality—delivering a strong return on investment while positioning the company for long-term competitiveness.
How Cflow Simplifies the PPAP Workflow
Cflow is a no-code workflow automation platform that enables manufacturers to digitize and streamline the Production Part Approval Process (PPAP). While it is not a PPAP-specific system like traditional PLM or QMS platforms, Cflow provides customizable workflow automation tools that replicate the full PPAP lifecycle — from document submission to final approval — in a controlled, audit-ready environment.
Here’s how Cflow simplifies each stage of the PPAP workflow:
1. Workflow Automation for Approval Routing
Cflow enables you to create automated, conditional workflows that route PPAP documents such as Process FMEAs, Control Plans, Dimensional Results, and Part Submission Warrants (PSWs) to the correct stakeholders — quality engineers, procurement officers, and suppliers.
- Eliminates manual email follow-ups.
- Enables sequential or parallel approvals.
- Keeps stakeholders accountable with real-time status updates.
2. Drag-and-Drop Form Builder for Standardised PPAP Submissions
With Cflow’s drag-and-drop form designer, you can create custom forms that align with the structure and fields of PPAP documents. Each form can be configured with mandatory fields, validations, and conditional logic.
- Standardises data capture for all 18 PPAP elements.
- Reduces submission errors and ensures completeness.
3. Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
To ensure data security and process integrity, Cflow includes role-based access controls that define who can view, edit, or approve each document or workflow step.
- Compliant with IATF 16949 and ISO 9001 requirements.
- Prevents unauthorised access to sensitive data.
4. Version Control and Audit Trails
Every document or form submitted in Cflow is automatically versioned, and each action is logged in an audit trail.
- Enables traceability for changes made during the approval process.
- Simplifies internal and external audits.
5. SLA-Based Task Monitoring and Escalations
Cflow lets you define Service Level Agreements (SLAs) to track how long each step in the PPAP approval takes. If deadlines are missed, automatic escalations and reminders are triggered.
- Ensures timely reviews and submission cycles.
- Improves supplier accountability and response times.
6. Integration with ERP and PLM Systems
Using Cflow’s API and webhook connectors, manufacturers can link the platform to ERP and PLM systems like SAP, Oracle, and Teamcenter.
- Automatically pulls part numbers, BOMs, and supplier details.
- Eliminates redundant data entry and reduces manual errors.
7. Centralised Repository for PPAP Documentation
All PPAP forms, attachments, and review notes are stored in a centralised, cloud-based repository within Cflow. This ensures fast document retrieval and permanent storage.
- Supports digital readiness for audits and customer inspections.
- Simplifies compliance with ISO 9001, IATF 16949, and OEM standards.
Conclusion
Manufacturers that rely on outdated PPAP processes are risking delays, non-compliance, and poor supplier coordination. By digitising the product part approval process with tools like Cflow, businesses can streamline approvals, reduce errors, and meet customer demands more efficiently. Cflow enables manufacturers to stay audit-ready, accelerate launches, and uphold quality standards at every step. Start a free trial of Cflow today.
FAQs
1. What documents are required in a Level 3 PPAP submission?
A Level 3 PPAP includes documents like design records, DFMEA, control plans, MSA, ISIR, and the PSW. It also requires submission of sample parts. This level provides full validation of the production process and product compliance.
2. How does automating PPAP improve compliance with industry standards?
Automation ensures traceability, version control, and timely approvals across all PPAP stages. It supports IATF 16949 and ISO 9001 compliance. Tools like Cflow minimise manual errors and keep audit records complete and accessible.
3. What are the key benefits of using a digital workflow for PPAP?
Digital workflows accelerate approvals, reduce manual tasks, and improve cross-team collaboration. They standardise submissions and offer real-time visibility into process status. The result is fewer delays, fewer errors, and better supplier accountability.
4. How does PPAP impact supplier performance?
PPAP helps suppliers adhere to quality standards and process consistency. It improves submission accuracy and accountability. This enhances trust, speeds up approvals, and strengthens supplier performance overall.
5. Can PPAP workflows integrate with ERP or PLM systems?
Yes, PPAP platforms like Cflow integrate with ERP and PLM systems to sync real-time part data. This eliminates duplicate entries and reduces errors. Integration ensures faster, more accurate, and consistent documentation across systems. Thanks for reading till the end. Here are 3 ways we can help you automate your business: Create workflows with multiple steps, parallel reviewals. auto approvals, public forms,
etc. to save time and cost. Get a 30-min. free consultation with our Workflow expert to optimize
your daily tasks. Explore our workflow automation blogs, ebooks, and other resources to master
workflow automation.
What should you do next?

Do better workflow automation with Cflow

Talk to a workflow expert

Get smarter with our workflow resources
Get Your Workflows Automated for Free!