AI vs RPA in Workflow Automation: Which is Better?

Key takeaways
- AI and RPA offer distinct advantages in workflow automation—AI brings intelligence and adaptability, while RPA delivers speed and consistency in rule-based tasks.
- RPA excels in structured, repetitive workflows, making it ideal for quick automation wins with minimal complexity.
- AI is best suited for unstructured, data-driven decision-making, enabling deeper insights and contextual actions.
- Cflow simplifies automation with AI-powered workflow creation, helping teams design intelligent, no-code workflows that scale with business needs.
As businesses face mounting pressure to optimise efficiency, reduce costs, and increase accuracy, workflow automation has become a key strategy for transformation. Two technologies stand at the forefront of this shift: Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Robotic Process Automation (RPA). While both aim to automate workflows, they function in fundamentally different ways—and choosing between them isn’t always straightforward.
For decision-makers and operations leaders, understanding the core differences, capabilities, and ideal use cases of AI and RPA is crucial. This blog dives deep into the AI vs RPA comparison, outlining which technology is better suited for your unique workflow needs and long-term business goals.
Understanding AI and RPA in Workflow Automation
AI and RPA are two core pillars of automation, but they solve different problems. Understanding how they work together—and independently—is essential for building the right automation strategy.
The global RPA market was valued at $22.80 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach approximately $211.06 billion by 2034, expanding at a CAGR of 25.01%.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is a rules-based automation technology that mimics human actions within digital systems. It follows predefined instructions to perform repetitive, structured tasks like data entry, invoice processing, and report generation. RPA excels at high-volume, routine processes where the steps are consistent and require little to no human judgment. It integrates easily with both legacy and modern applications, making it ideal for quickly automating back-office functions.
Artificial Intelligence (AI), by contrast, brings cognitive capabilities into automation. It enables machines to simulate human intelligence—learning from data, recognising patterns, and making decisions. In workflow automation, AI adds depth and flexibility by analysing unstructured inputs, predicting outcomes, and adapting to new scenarios. Unlike RPA, which can only follow programmed rules, AI systems evolve over time using machine learning, natural language processing, and decision logic.
For every $1 invested in generative AI, companies are realising an average return of $3.70, with top-performing organisations achieving up to $10.30.
Combined, AI and RPA can create intelligent automation systems where RPA handles structured, repeatable tasks, and AI manages complex workflows involving reasoning, interpretation, and predictive decision-making. For example, RPA might extract data from invoices, while AI interprets sentiment in customer emails or recommends workflow adjustments based on historical trends.
This foundational understanding of the difference between AI and RPA in automation helps organisations choose the right approach—or blend of both—for achieving end-to-end efficiency in their business operations.
Difference Between AI and RPA in Automation
Though often used together, AI and RPA are fundamentally different in how they function and what they automate. This comparison highlights their core distinctions to help guide technology selection.
| Criteria | Robotic Process Automation (RPA) | Artificial Intelligence (AI) |
| Nature of Technology | Rule-based automation | Cognitive and learning-based automation |
| Functionality | Mimics human actions using predefined scripts | Simulates human intelligence to learn, reason, and adapt |
| Task Complexity | Ideal for simple, repetitive, and structured tasks | Handles complex, decision-based, and unstructured tasks |
| Data Type | Structured data only | Structured and unstructured data |
| Learning Ability | No learning capability—follows fixed logic | Learns from data using ML algorithms and improves over time |
| Flexibility | Limited to predefined workflows | Adapts to new inputs and evolving scenarios |
| Integration Needs | Easy to integrate with existing systems | May require more setup and training time for effective integration |
| Implementation Time | Faster to deploy and scale | Takes longer due to training and data requirements |
| Cost Consideration | Lower initial investment; quick ROI | Higher upfront cost, better long-term value through insights |
| Example Use Case | Automating invoice data entry or form filling | Analysing customer behaviour or processing natural language inputs |
Pros and Cons of AI vs RPA
Understanding the strengths and limitations of both AI and RPA helps organisations choose the right technology—or a hybrid approach—for their automation strategy.
RPA: Pros
- Quick Deployment: Fast implementation with minimal technical complexity, ideal for short-term automation goals.
- High ROI: Delivers significant cost savings for repetitive, rule-based processes like data entry, reconciliation, and approvals.
- Legacy System Integration: Works effectively with existing legacy applications without major system overhauls.
RPA: Cons
- Limited Intelligence: Cannot handle tasks that require decision-making or adapt to changing process conditions.
- Structured Data Only: Incapable of processing unstructured data like scanned documents, emails, or voice inputs.
- Fragile at Scale: Prone to failure when faced with exceptions or changes in input formats, requiring frequent adjustments.
AI: Pros
- Handles Complexity: Excels at decision-based tasks involving large datasets and complex logic.
- Self-Learning Capabilities: Improves performance over time using machine learning algorithms.
- Advanced Features: Enables predictive analytics, natural language processing, image recognition, and process optimisation.
AI: Cons
- Data-Intensive: Requires large, high-quality datasets for effective model training and accuracy.
- Longer Implementation: Deployment timelines are extended due to model development, testing, and integration needs.
- Higher Initial Cost: Greater upfront investment is needed for setup, skilled personnel, and data infrastructure.
AI vs RPA Use Cases: Understanding the Strategic Divide
When it comes to automation in large enterprises, it’s crucial to differentiate between Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and Artificial Intelligence (AI). While they are often used together, their applications, capabilities, and ideal use cases vary significantly. Understanding where each excels allows business leaders to make strategic decisions that maximise ROI and operational efficiency.
Where RPA Works Best?
Robotic Process Automation is designed for rule-based, repetitive tasks that follow a structured format. It mimics human interactions with digital systems, making it ideal for processes with predictable workflows and minimal variability.
1. Payroll Processing:
RPA can automate end-to-end payroll tasks—such as extracting timesheet data, calculating pay, and generating payslips. It ensures consistency, reduces errors, and saves time, particularly in large organisations with thousands of employees.
2. Data Migration:
Moving data between systems—especially during system upgrades or migrations—can be tedious and error-prone. RPA bots efficiently transfer large volumes of structured data between legacy systems, databases, or cloud applications with minimal manual input.
3. Email Response Automation:
For transactional or rule-based queries (e.g., password resets, invoice requests), RPA bots can auto-respond using predefined templates. This reduces the load on support teams and ensures quick resolution for high-volume inquiries.
RPA excels in operational efficiency, offering speed and accuracy in tasks that don’t require reasoning or learning. However, it’s limited when facing unstructured data or dynamic decision-making.
Where AI Shines
Artificial Intelligence, on the other hand, thrives in scenarios requiring data interpretation, learning, and context-based decision-making. It enables enterprises to automate more complex, cognitive functions that go beyond simple task repetition.
1. Customer Sentiment Analysis:
AI can analyse thousands of customer interactions—emails, chat logs, surveys—to detect tone, emotion, and satisfaction. This helps enterprises understand sentiment trends and proactively address service issues or product concerns.
2. Sales Forecasting:
AI-driven predictive analytics use historical data, market trends, and external variables to deliver accurate sales forecasts. This informs better inventory planning, resource allocation, and strategic decision-making—particularly valuable in volatile markets.
3. Intelligent Document Processing (IDP):
AI combines OCR (Optical Character Recognition), NLP, and ML to extract data from unstructured documents like contracts, invoices, and forms. It not only reads but also understands context, enabling accurate classification and integration with downstream systems.
In essence, AI enables decision-making, pattern recognition, and adaptability, making it the go-to solution for processes involving variability, context, or large volumes of unstructured data.
End-to-end workflow automation
Build fully-customizable, no code process workflows in a jiffy.
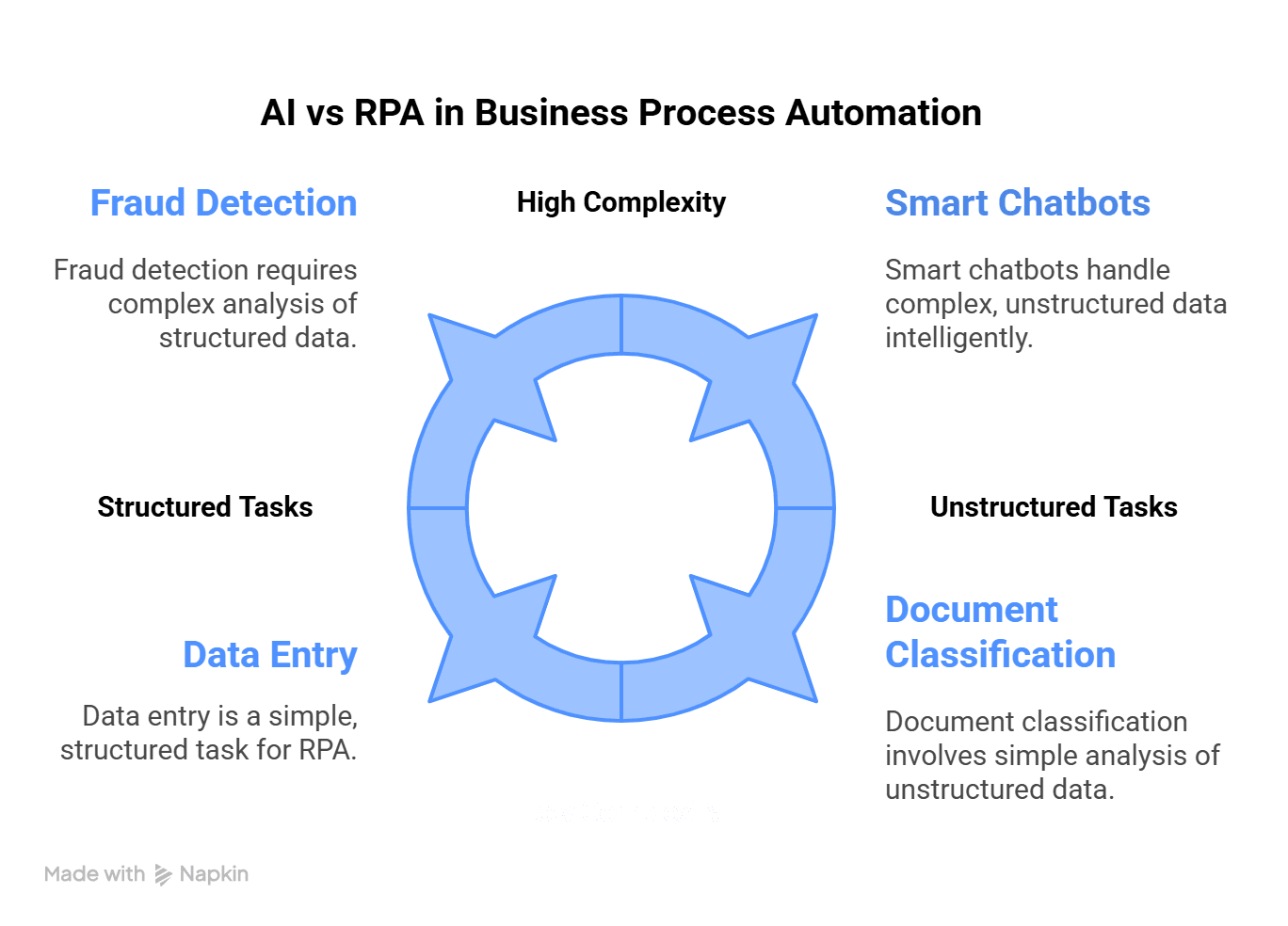
AI vs RPA in Business Process Automation: Choosing the Right Fit
When it comes to business process automation, the decision between Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Robotic Process Automation (RPA) depends largely on the nature and complexity of the tasks you aim to automate.
RPA is ideal for structured, repetitive operations where steps are clearly defined and predictable. These software bots act like digital assistants, executing routine tasks with speed and precision, without disrupting existing systems.
Use RPA when:
– Tasks follow clear, rule-based logic.
– Data involved is structured and consistent.
– Processes include data entry, payroll, or invoice processing.
– You need fast deployment with minimal IT effort.
In contrast, AI adds intelligence to automation. It’s designed to handle variability, make contextual decisions, and continuously improve based on data patterns. If your workflows are dynamic or data is unstructured, AI provides the flexibility and learning capabilities you need.
Use AI when:
Processes require interpretation, decision-making, or pattern recognition.
– Data sources are unstructured (emails, PDFs, audio, etc.).
– You need automation that adapts over time and interacts intelligently.
– Applications include fraud detection, smart chatbots, or document classification.
For organisations aiming at enterprise-wide transformation, the most strategic approach is to combine both technologies. Known as hyperautomation, this approach unifies the structured precision of RPA with the cognitive capabilities of AI, enabling businesses to automate a broader spectrum of workflows—both simple and complex.
There’s no one-size-fits-all answer. Instead, it’s about aligning the right tool to the right task to maximise efficiency, intelligence, and long-term scalability.
The Future of AI and RPA in Workflow Management
In the near future, organisations won’t just automate repetitive tasks—they’ll orchestrate end-to-end processes that evolve in real-time. With AI-powered bots analysing data, predicting outcomes, and making decisions, businesses can unlock continuous improvement without human intervention. For instance, imagine a claims processing workflow that not only extracts data but also detects anomalies, routes cases intelligently, and learns from outcomes to improve future decisions.
As IPA matures, its impact will go beyond efficiency. It will drive resilience, agility, and personalisation in operations. Workflows will self-heal, identify bottlenecks before they occur, and personalise experiences for customers and employees alike.
Key trends shaping this future include:
- Hyperautomation: Automating every possible business process using AI, RPA, and advanced analytics.
- AI-Augmented RPA: Bots that can interpret unstructured data, such as emails or scanned documents, and act contextually.
- Autonomous Decision-Making: AI models embedded within workflows to make complex, high-impact decisions without delays.
- Low-Code/No-Code + IPA: Business users will increasingly build and modify workflows using visual tools, further democratizing automation.
Ultimately, the future of workflow management lies in systems that think, learn, and adapt—freeing human teams to focus on creativity, innovation, and strategic growth. Businesses that embrace this shift early will lead the charge into a new era of operational excellence.
How Cflow Supports AI-Powered Workflow Creation
Cflow is a no-code workflow automation platform that empowers teams to automate business processes with speed and precision. What sets Cflow apart is its AI-powered workflow creation, enabling users to build workflows faster and smarter—without relying on developers or writing any code.
Key Features of Cflow:
1. AI-Powered Workflow Creation: Instantly generate workflow structures based on user input and logic suggestions—saving time and improving accuracy.
2. Visual Workflow Builder: Drag-and-drop interface for designing, customising, and managing workflows with ease.
3. OCR for Document Processing: Extracts data from scanned forms and documents, converting them into usable workflow inputs.
4. Real-Time Dashboards: Track approvals, task progress, and bottlenecks with visual reporting tools.
5. Mobile Accessibility: Access, approve, or update workflows on the go through a mobile-friendly platform.
6. Seamless Integrations: Connects easily with ERP, CRM, and cloud-based applications for end-to-end automation.
7. Enterprise-Grade Security: Offers user-level access controls, audit logs, and data protection features.
Why Cflow?
- Start quickly: AI helps you create intelligent workflows in minutes.
- Build without code: Empower business users to take ownership of automation.
- Scale with confidence: Evolve workflows as your business grows—without starting from scratch.
Book your free trial of Cflow and start building intelligent workflows today.
Final Thoughts
AI and RPA are not competing technologies—they’re complementary. To truly transform operations, businesses should evaluate workflows holistically and deploy the right mix. Start small with RPA, expand with AI, and scale with a unified platform.
For enterprises looking to future-proof their automation strategy, Cflow offers the perfect foundation for smarter, faster, and more adaptive workflows.
Start your journey with Cflow today — book a demo or start now with a free trial.
FAQs
1. Can RPA be used without AI?
Yes. RPA can function independently to automate rule-based tasks without requiring AI capabilities.
2. Is AI more expensive than RPA?
Generally, yes. AI systems require more data, training, and resources, making them costlier to implement than RPA.
3. Should businesses choose AI or RPA first?
Start with RPA for immediate efficiency gains. Use AI later to scale and optimise processes that involve judgment and learning.
What should you do next?
Thanks for reading till the end. Here are 3 ways we can help you automate your business:

Do better workflow automation with Cflow
Create workflows with multiple steps, parallel reviewals. auto approvals, public forms, etc. to save time and cost.

Talk to a workflow expert
Get a 30-min. free consultation with our Workflow expert to optimize your daily tasks.

Get smarter with our workflow resources
Explore our workflow automation blogs, ebooks, and other resources to master workflow automation.