Optical Character Recognition (OCR): What It Is & How It Works?

Key takeaways
- OCR (Optical Character Recognition) automates text extraction from scanned documents, converting printed and handwritten content into machine-readable and editable formats.
- This technology enhances efficiency by reducing manual data entry, improving accuracy, and streamlining document processing across various industries.
- Different OCR techniques, including ICR and deep learning OCR, enable recognition of complex handwriting, multilingual text, and structured documents.
- AI-powered OCR continuously learns and improves accuracy, making it essential for automation in finance, healthcare, legal, and logistics sectors.
What is Optical Character Recognition?
OCR (Optical Character Recognition) is an advanced technology that converts printed, handwritten, or scanned text from images, PDFs, and paper documents into machine-readable and editable formats. This process enables businesses to digitise physical records, making them searchable, editable, and easily stored in digital databases.
An OCR system works by analysing character patterns within an image, recognising text structures, and converting them into a digital format. It plays a crucial role in automating data extraction, reducing manual entry errors, and improving document processing efficiency. Without OCR, businesses would struggle with inefficiencies related to manually inputting data from printed documents.
For example, a financial institution processing thousands of loan applications daily can use OCR to extract critical information from scanned forms automatically. This significantly reduces processing time, enhances accuracy, and improves overall operational efficiency. OCR is widely used across industries like banking, healthcare, logistics, and legal services, enabling organisations to streamline workflows and enhance productivity.
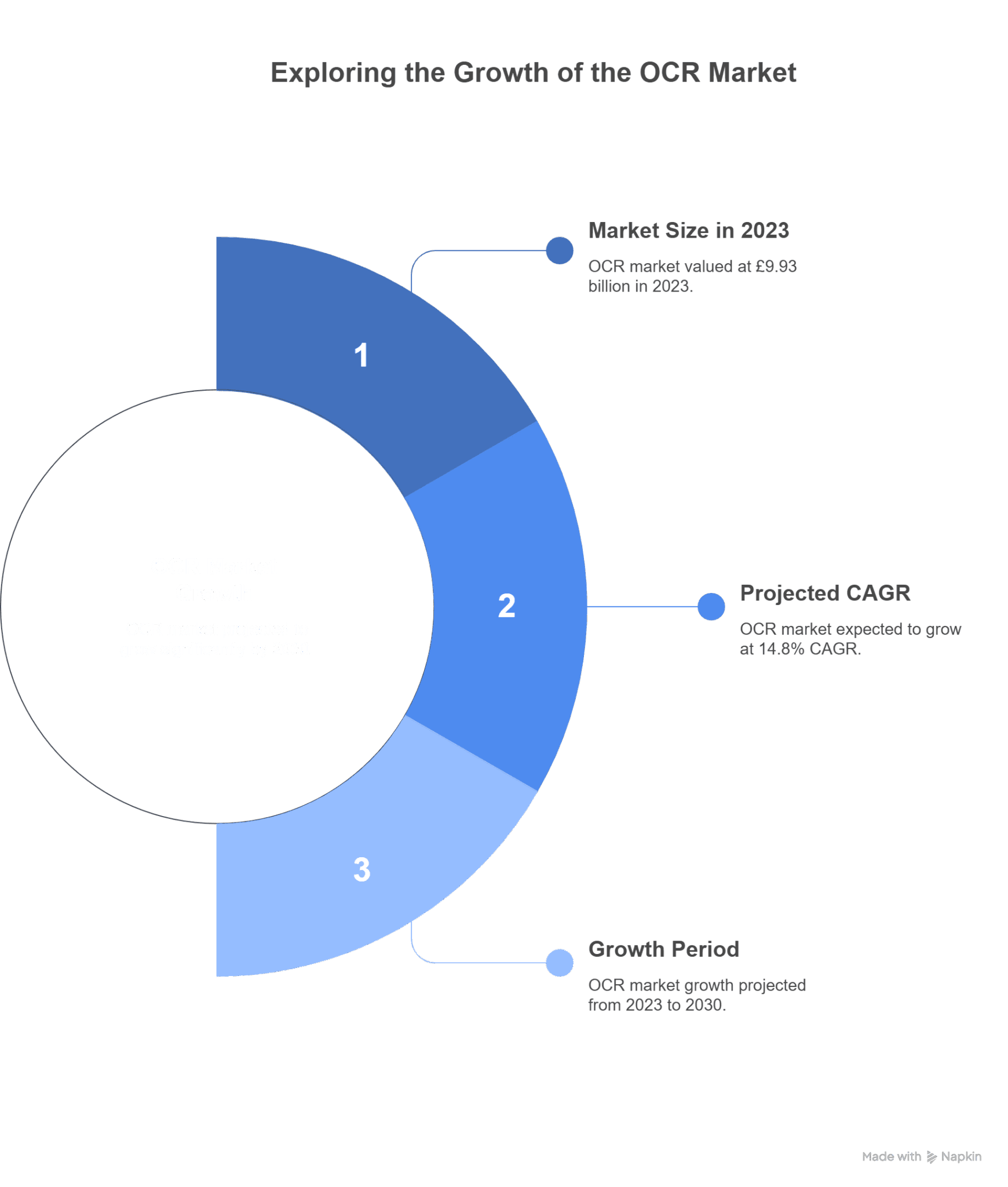
According to a report by Grand View Research, the global OCR market was valued at approximately USD 12.56 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 14.8% from 2023 to 2030.
How does OCR Work?
OCR (Optical Character Recognition) technology converts printed, handwritten, or scanned text into machine-readable and editable formats by following a structured process. It involves multiple steps to accurately recognise characters and transform them into digital text.
1. Image Preprocessing – The OCR software enhances the scanned document by removing noise, adjusting contrast, and correcting distortions. This step improves text recognition accuracy.
2. Text Detection – The system identifies text regions within the document and separates them from non-text elements like images, backgrounds, and borders.
3. Character Recognition – OCR software uses pattern-matching and machine learning algorithms to analyse individual characters, numbers, and symbols. It then converts them into a digital format.
4. Post-Processing and Error Correction – The recognised text is refined using context-based error detection, spell check, and language models to ensure accuracy.
5. Text Output – The final extracted text is stored in an editable format such as Word, Excel, or searchable PDFs for easy access and processing.
Types of OCR Techniques
OCR technology has evolved significantly, offering different techniques to recognise printed, handwritten, and structured text with greater accuracy. Various OCR methods are used across industries like finance, healthcare, and legal services to automate document processing and data extraction.
Below is a comparison of the main OCR techniques and their functionalities:
| OCR Technique | Description |
|---|---|
| Simple OCR (Pattern Matching OCR) | Compares scanned text with a stored database of character patterns. Works well with standard fonts but struggles with handwriting. |
| Feature Extraction OCR | Identifies characters by analysing unique features like lines, curves, and intersections, making it adaptable to various fonts. |
| Intelligent Character Recognition (ICR) | An advanced technique that recognises handwritten text and improves accuracy over time using machine learning. |
| Intelligent Word Recognition (IWR) | Recognises entire words instead of individual characters, making it effective for cursive handwriting and loosely structured text. |
| Optical Mark Recognition (OMR) | Detects marks, checkboxes, and multiple-choice answers, which are commonly used in surveys, exams, and voting systems. |
| Zonal OCR | Extracts text from specific regions of a document, automating data entry in invoices, forms, and ID documents. |
| Contextual OCR with AI (Deep Learning OCR) | Uses AI and deep learning to recognise complex handwriting, distorted text, and multiple languages while improving accuracy over time. |
Key Benefits of OCR Technology
OCR (Optical Character Recognition) has become a transformative tool for businesses looking to enhance efficiency and accuracy in document processing. By automating text extraction and reducing reliance on manual data entry, OCR plays a crucial role in digital transformation. Below are seven major benefits of OCR, backed by credible sources:
1. Minimises Time Spent on Manual Data Entry
OCR eliminates the need for manual data input, significantly cutting down the time spent on processing documents. According to McKinsey & Company, automation technologies, including OCR, have the potential to raise global productivity growth by 0.8 to 1.4 percent annually.
2. Boosts Operational Efficiency
With OCR, businesses can process large volumes of paperwork quickly and efficiently, leading to faster turnaround times. Deloitte reports that 53% of organisations have already implemented workflow automation to enhance efficiency.
3. Accelerates Digital Transformation
OCR is a key driver of digital transformation, helping companies transition from paper-based processes to fully digital workflows. Research from Deloitte highlights that 92% of organisations consider cloud-based and automation solutions essential for digital transformation.
4. Reduces Business Costs
By automating document processing, OCR helps businesses cut labour costs associated with manual data entry. A Deloitte survey found that companies implementing automation solutions have achieved an average cost reduction of 24%.
5. Enhances Data Accuracy and Integrity
Manual data entry is prone to human errors, which can lead to costly mistakes. OCR significantly improves data accuracy by minimising manual intervention. According to McKinsey, businesses that implement AI-powered workflow automation experience fewer data processing errors and increased reliability in decision-making.
6. Improves Customer Experience
By streamlining document processing, OCR enables businesses to provide faster, more efficient customer service. According to Adobe, companies that prioritise automation and efficiency see a 1.6x increase in customer satisfaction and 1.9x higher average order values.
7. Enables Innovation and Business Scalability
OCR frees up employees from repetitive tasks, allowing them to focus on strategic growth initiatives. Research from Statista shows that 35% of organisations recognise automation technologies like OCR as key drivers of business innovation and scalability.
Traditional Approaches to OCR
OCR technology has come a long way from its early days when text recognition relied on rigid, rule-based techniques with limited accuracy. Traditional OCR methods primarily used pattern matching and matrix-based recognition, where scanned characters were compared to pre-stored templates of known fonts and symbols. While this approach worked well for structured, printed text, it struggled with variations in handwriting, font styles, and poor-quality scans.
1. Pattern Matching and Matrix-Based Recognition
One of the earliest OCR methods was pattern matching, where scanned characters were compared against a database of pre-defined character templates. If the scanned character matched an existing template, it was recognised. While this method worked well for uniform printed text, it failed with handwritten or distorted fonts.
2. Matrix-based recognition
refined this approach by dividing characters into a grid and comparing pixel structures, but it was still highly sensitive to noise and inconsistencies in scanned documents.
3. Feature-Based OCR
As an improvement over pattern matching, feature-based OCR analysed individual components of characters—such as lines, curves, and intersections—rather than matching entire letters to a predefined template. This allowed for more flexibility in recognising different fonts and sizes, but it still struggled with complex scripts, handwritten text, and multi-language documents.
4. Rule-Based OCR with Contextual Analysis
To enhance recognition accuracy, rule-based OCR incorporated basic linguistic rules and contextual analysis. This method helped correct errors by predicting words based on predefined grammar and dictionaries. However, this approach required extensive manual setup, making it inflexible and impractical for large-scale implementations.
Despite these advancements, traditional OCR methods were largely limited by their reliance on clean, high-resolution scans and standardised fonts. They were ineffective for handling diverse handwriting styles, distorted images, or complex document formats, which led to the need for more intelligent OCR solutions.
Adoption Across Key Industries
Various UK industries have integrated OCR technology to streamline processes and improve accuracy:
1. Banking and Financial Services: Financial institutions utilise OCR to automate data extraction from cheques, loan applications, and statements, reducing processing time and errors.
2. Healthcare: OCR aids in digitising patient records, prescriptions, and insurance claims, enhancing accessibility and regulatory compliance.
3. Retail and E-commerce: Retailers use OCR for inventory tracking, invoice processing, and extracting data from receipts, improving operational agility.
4. Legal Services: Law firms convert legal documents into searchable formats using OCR, improving case management and document accessibility.
How Has OCR Evolved?
OCR technology has significantly advanced through artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and deep learning, making today’s systems far more adaptive and accurate. Modern OCR platforms no longer rely on rigid templates but instead use AI to recognise diverse text patterns.
1. Machine Learning-Based OCR
Machine learning-based OCR trains itself on extensive datasets of fonts and scripts. This enables recognition of varied handwriting, distorted fonts, and diverse languages, improving accuracy across industries.
2. AI and Neural Network-Powered OCR
Solutions like Google’s Tesseract OCR or Microsoft’s Azure OCR apply deep neural networks for recognising unstructured or poorly scanned documents. They continuously learn from new data to improve results.
3. Intelligent Character Recognition (ICR)
ICR allows real-time recognition of handwritten content, adapting to cursive and stylised writing. This is particularly valuable in UK industries like banking (cheques), healthcare (prescriptions), and law (case files).
4. Cloud-Based OCR for Real-Time Processing
With cloud technology, OCR is now scalable and accessible. UK businesses benefit from fast, remote processing of documents without on-premise infrastructure.
5. OCR with Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Modern OCR tools combine NLP to understand sentence context and grammar, providing better accuracy in data extraction and compliance-driven document handling.
Limitations of OCR Technology
Despite innovation, OCR has limitations that affect its overall performance:
- Inconsistent Scan Quality – Low-resolution or blurry images hinder recognition accuracy.
- Handwriting Recognition Issues – Variations in handwriting remain a challenge.
- Complicated Document Structures – Mixed layouts like tables and columns affect consistency.
- Language and Symbol Restrictions – Non-Latin characters can reduce recognition performance.
- Character Confusion – Similar characters like ‘I’ and ‘l’ or ‘0’ and ‘O’ can be misread.
- Resource-Intensive Processing – High computing power may be needed for large batches.
- Data Security Risks – Sensitive documents must be handled with strict compliance to UK GDPR.
Cflow and OCR: Enhancing Workflow Automation
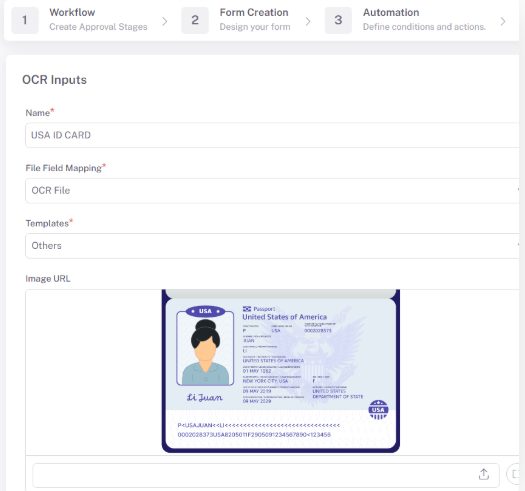
As UK businesses embrace digital transformation, integrating OCR (Optical Character Recognition) into workflow automation is key to reducing costs and manual errors. Cflow, a no-code workflow automation platform, supports OCR to extract and manage data from scanned documents, images, and PDFs.
How Cflow Utilises OCR in Workflows
Cflow extracts text from structured and unstructured sources, eliminating the need for manual data input. OCR data can trigger automated workflows, including approval chains, notifications, and document storage processes.
OCR Capabilities Within Cflow
- Automated Text Extraction – Converts handwritten and printed text to digital.
- Improved Accuracy – Reduces human error in data capture.
- Seamless Workflow Integration – Sends data directly to workflow steps.
- Faster Document Processing – Cuts down approval and response times.
- Secure and Organised Storage – Helps with GDPR compliance and retrieval.
By leveraging OCR, Cflow enables UK organisations to automate document workflows in finance, HR, healthcare, and legal domains with minimal effort.
Conclusion:
OCR has revolutionised how UK businesses manage documents—speeding up processes, improving accuracy, and enabling digital-first operations. With advancements in AI and NLP, OCR continues to evolve as an essential tool for modern enterprises.
Book a demo or try out the free trial of Cflow to experience how OCR can optimise your workflows.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What does OCR mean, and how does it work?
OCR (Optical Character Recognition) converts printed, handwritten, or scanned text into machine-readable formats. It works by analysing patterns and outputs digital formats like Word, Excel, or searchable PDFs.
2. OCR—What does it stand for, and what is its purpose?
OCR stands for Optical Character Recognition. It digitises physical documents, making them editable, searchable, and easy to store electronically.
3. What is an Optical Character Reader (OCR), and where is it used?
OCR systems scan and convert text into digital formats. It’s used in UK sectors like banking, healthcare, law, and logistics to automate processes.
4. How accurate is OCR technology, and what factors affect its performance?
OCR accuracy depends on image quality, font clarity, and language. AI-powered OCR improves performance even with handwriting or complex layouts.
5. What are the main benefits of using OCR for businesses?
OCR helps automate data entry, reduce errors, accelerate workflow, and improve compliance, essential for UK organisations embracing digital transformation.