What is BPMS? (Business Process Management System)

Key takeaways
- Modern businesses must frequently review their processes to stay efficient, agile, and competitive in evolving markets.
- A Business Process Management System (BPMS) enables automation, visibility, and control across key business functions like HR, finance, and operations.
- BPMS platforms follow a 5-stage approach: define, design, automate, analyse, and measure for continuous improvement.
- Using BPMS improves team collaboration, reduces errors, and boosts employee satisfaction by eliminating repetitive manual tasks.
- Top BPMS tools for 2025 include Cflow, Appian, Bizagi, Genpact, Pegasystems, and IBM—each suited for specific business needs.
- Selecting the right BPMS requires focusing on must-have features like visual workflows, role-based access, analytics, and third-party integration.
When was the last time you reviewed your business processes to evaluate their efficiency and effectiveness? 6 months back? 12 months back, or even before? The sheer volume of work involved in process review and audit can put off even the most diligent worker.
This is where a BPMS comes into play. Managing your business processes can never get easier than this. You can review, track, monitor, and improve your business processes with BPMS.
Now, what is BPMS, and why is it important for your business? Read on to know.
What is BPMS?
BPMS stands for “Business Process Management System” or “Business Process Management Software”, which can significantly improve the efficiency of business processes. Let us first understand the meaning of BPMS. A BPMS is an automation tool that helps analyse, model, implement, and monitor business processes.
BPM’s main focus is to identify the vulnerabilities in everyday business practices that cost time and money for the business and to control them. BPMS helps in streamlining the process of business operations and improving cross-team collaboration and communication. In the process of improving the operational efficiency of the business, the quality of customer service is also improved.
BPMS creates an infrastructure that promotes business agility, flexibility, scalability, and adaptability. The key advantage of BPMS is that its users have the opportunity to play an active part in the improvement of business processes using simple and intuitive tools. Before creating automated BPM workflows, processes need to be documented so that areas for improvement can be identified.
BPMS can be used to create process models and reviewed by stakeholders for an accurate depiction of the process. The most common format in business process models published is business process mapping notation (BPMN).
Where can common BPMS solutions be applied?
BPMS is mostly applied to processes in an organisation that are repeatable, carried out on a regular basis, and have predictable outcomes. Some common uses for BPMS are enhancing the productivity of business functions like the purchase order process, content marketing, finance and accounting, and HR and Admin.
All these processes, when managed using archaic methods, lack the visibility and transparency required to know which stage the project/process is in. The lack of visibility makes it difficult for managers to understand what is happening at each step and how well the team is performing. The methodology of BPM helps organisations optimise their performance by improving the efficiency and effectiveness of their business processes.
The use cases of business process management systems are endless and keep increasing as different business ideas emerge. BPM is often considered to be the same as BPMS. BPM is a practice carried out by people, while BPMS is a set of technical resources that help practitioners achieve their goals. To produce better performance, organisations leverage BPM to streamline their processes and process automation to automate tasks that are repeatable in nature and produce predictable outcomes.
Organisations that wish to maximise efficiency by enhancing process management and encouraging collaboration between individuals, procedures, and information systems go for automation using BPM tools.
Business Process Management System (BPMS) Works in 5 Stages
1. Process definition and analysis
A process may be considered as a sequence of activities that are executed in a specified order to obtain a specific result. Before we automate workflows, we need to first define and document the process. Process documentation requires collaboration and planning amongst stakeholders to figure out the most efficient and suitable actions for fulfilling the task. Process flows can be recreated within a BPMS and reviewed by relevant personnel to ensure that the process is effectively portrayed.
2. Process design (development)
Once the process has been defined and documented, it becomes easy to determine the most efficient way to improve process outcomes. The new process can be built with a process designer tool like Cflow. The visual process designer in Cflow makes it simple and quick to create process workflows. The process can be defined based on a set of rules and elements provided in the visual process builder. Designing a process based on BPM is of great advantage as it enables the user to make amendments to the weak areas before implementation.
3. Automation
Automation is how a process is performed with minimal human intervention. Automation of process workflows helps businesses better manage and optimise their workflows. Creating automated workflows involves assembling actions and inputting the mechanisms that drive these actions, with the help of visual workflows that mimic the behaviour of the business process.
Ideally, tasks that are repetitive, produce predictable outcomes, and require no human intelligence are the ones best suited for automation. The primary aspect of process automation is offloading most of the rote work and task management to a BPM solution programmed with business rules and automated triggers.
4. Analytics
BPMS tools offer multiple levels of reporting and the ability to integrate with reporting tools for gathering process performance analytics. Reports based on key performance indicators provide insights into process performance and the performance of teams and individuals. Analytics of process data is useful in identifying process inefficiencies and operational bottlenecks. Armed with analytics data, managers can take corrective measures to improve process performance.
5. Measurement
As with any business improvement effort, measurement with BPM automation is critical. It is important to first decide on what to measure. While deciding this, you need to bear in mind not to take an unscripted approach that catalogues a wish list of KPIs. Taking this approach results in too long a list of KPIs, KPIs that provide low business value, or KPIs that are not aligned with high-level business objectives. KPIs must be SMART – specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound.
BPM Suite Versus BPMS
A BPM suite and BPMS are often assumed to be the same thing. There are, however, some subtle differences between the two. A BPM suite is a set of integrated tools for the design, execution, and management of a process. A BPMS, on the other hand, is a platform that runs processes.
BPMS may be considered as a foundation for building a BPM suite. A BPMS does not have all the capabilities for running a business efficiently. A BPM suite offers a wide range of capabilities that help you manage the entire process lifecycle – from planning through execution and optimisation. Advanced features like automation and analytics are offered by BPM suites to personalise customer experiences across digital channels.
BPMS are the platforms that run processes. They provide the tools to manage and automate business processes by allowing users to take advantage of BPM benefits. BPMS provides the infrastructure that supports BPM and associated tools. It supports process modelling, workflow automation, and complex event processing.
BPMS provides tools for managing the development and maintenance of business process models, while a BPM suite integrates both systems to create an end-to-end solution for automating the entire organisation’s workflow.
Types of BPMS Solutions
When choosing a BPMS for your organisation, it is important to know the types of BPMS available to make the right choice. There are mainly two types of BPMS: enterprise BPMS and open-source BPMS.
Enterprise BPMS
This is typically an on-premise solution that is used by large organisations for managing complex enterprise-level business processes and requirements. These solutions provide a high degree of flexibility and customisation to business processes. Enterprise BPMS solutions require more time and effort to implement and maintain.
Open source BPMS
The open-source alternative to enterprise BPMS can cost much less than commercial products. Outright purchases of these solutions can be done instead of paying per-user licenses or annual or monthly subscriptions. These solutions are more customizable compared to their commercial counterparts because they are built from scratch instead of being derived from prebuilt components like those used in proprietary software platforms.
There is another classification of BPMS based on the processes they handle – Integration-centric, Human Centric, and Document Centric. Integration-centric BPMS handles processes that require minimal or no human interaction, and it depends on the integration of computer and internet-based apps.
Document-centric BPMS handles process documentation and approvals. Multiple approvals at each point of the workflow are characteristic of this type of BPMS. Human-centric BPMS is a more direct approach where humans make important decisions at each step of the workflow. A visual interface guides them in the decision-making process.
Why is BPMS Important for your Business?
A business process management system improves and optimises processes systematically. Processes that can derive maximum benefit by implementing BPMS include HR, Sales, Compliance management, Employee Onboarding, Project management, Procurement, and Finance.
Who can use BPMS?
Irrespective of the type and size of the business, processes are the core. So, a BPMS can be used by any kind of business to automate processes and streamline operations.
Now, why is BPMS important for your business? To remain competitive and sustain in today’s super competitive business environment, businesses need to perform at optimal levels – every single time! Sticking to archaic manual methods of managing and running a business may seem simple and cost less, but in reality, they are eating into productivity and business budgets.
Here are 5 reasons why BPMS is important for your business
1. Enhances Team Collaboration
BPMS boosts internal communication within teams. It helps the team coordinate multiple functions between employees in different business units. Sharing information across various business functions is a breeze with BPMS. Department silos are broken down and decision-making is accelerated by a BPMS. Both internal collaboration between employees and external collaboration between the organisation, stakeholders, and customers are enhanced by BPMS.
2. Simplifies process improvement
Business processes need to be reviewed and improved on a regular basis for optimal business performance. Especially in businesses that grow rapidly, processes have to adapt to changing requirements. And if you are going to rely on traditional methods, you are going to be left behind in the rat race.
BPMS brings in the flexibility and adaptability required for adapting to changing/growing business environments. Moreover, the review of processes to identify redundancies and inefficiencies is greatly simplified by BPMS. You can adapt quickly and deliver a superior customer experience when you have a BPMS.
3. Improves employee satisfaction
An organisation that does not engage its employees or underutilises their potential is at risk of attrition and slowdown. When employees are made to work on rote tasks that do not utilise their potential, it is natural that they feel dejected and frustrated with their work. Employees who are stuck in such a boring and monotonous work pattern either leave the organisation or perform poorly. BPMS automates rote and low-value processes so that employees can focus on important, strategic work that makes them feel valued and utilises their skills optimally.
4. Optimises process performance
When redundant steps in a process are eliminated, what remains is a process that performs optimally! This is what BPMS does to business processes. By automating repetitive steps in a process, BPMS streamlines the process for maximum efficiency. Consistency of the process is also greatly improved by implementing a Business Process Management System.
5. Reduces errors and inaccuracies
Business functions like finance and accounting involve a lot of data validation and updating. When an employee skims through huge volumes of data, the chances of mistakes and overlooks are higher. When such data-intensive processes are automated, the error margins are significantly lower. By eliminating the human element from tedious data handling processes, accuracy and reliability increase exponentially.
Where Does BPMS Add Value?
As mentioned earlier, business processes that are repeatable and produce predictable outcomes are best suited for BPMS. Let us look at some of the common processes that can benefit from BPMS.
Purchase order process
Fulfilling purchase orders is quite a tedious process; necessary details can get lost, or wrong invoices could be paid, or there could be a mismatch between the PO and the Invoice. BPMS can take care of such issues. From the creation of the purchase order to approval, from order processing to payment, BPMS ensures seamless processing of purchase orders by automating tasks.
Healthcare management
Admission and discharge in a healthcare facility happen hundreds per day. The admission process involves several stages where information needs to be gathered, recorded, and shared. Business Process Management System can simplify the admission and discharge process by automating data gathering and management, for a stress-free experience for the patient and the hospital.
Content marketing
The seemingly straightforward content marketing process is much more complex and longer than it may the eye. There are several stages in this process: writing content to match the brief, reviewing and editing content, designing, publishing, and monitoring content performance. BPMS ensures a smooth flow from one stage to another and helps spot and rectify redundancies and inefficiencies.
7 Important Benefits of BPMS
By now, you must have got a handle on how BPMS improves business performance. What are the benefits of BPMS?
- Boosts process efficiency and productivity by automating rote tasks
- Minimises process cost and reduces execution time by cutting out redundant steps
- Improves the agility and flexibility of business processes
- Strengthens regulatory compliance of business processes
- Increases profitability by eliminating redundant steps
- Deepens visibility across the process
- Increases the security of process data by providing role-based access.
End-to-end workflow automation
Build fully-customizable, no code process workflows in a jiffy.
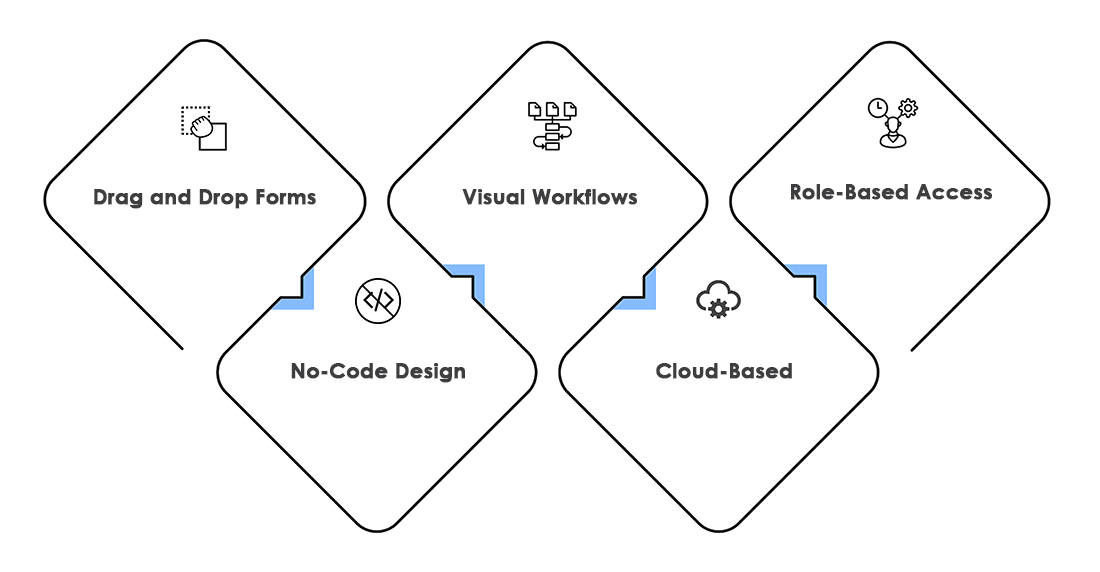
Must-Have Features of a Common BPMS
Choosing the right BPMS for your business can be tricky. We have put together a list of must-have features of BPMS to help you make the decision.
Visual workflow builder
The main reason you go for BPMS is to improve process efficiency. The Business Process Management System tool must be user-friendly, with drag-and-drop functionality for creating workflows. Integrating business rules with workflows must be a simple and quick process. Ample process modelling options, easy definition of sub-processes, easy task delegation and escalation, and seamless integration with third-party apps are some of the features that the workflow builder must have.
Role-based access
Process data must be handled with utmost safety and security. Access to sensitive information must be restricted to relevant users only. The Business Process Management System must provide role-based access to data to prevent any misuse of data.
Process monitoring dashboard
The Business Process Management System dashboard must provide robust process monitoring capabilities that enable users to stay on top of process execution, status, and any performance issues. Restarting a specific process or deploying new processes, or clearing bottlenecks must be an easy and quick task.
Alerts and notifications
Stakeholders of the process must be duly alerted and notified of any pending tasks on their end. They should not have to plough through their inboxes to locate email trails for approvals or review.
Third-party integrations
Automation of a process requires integration with third-party applications. The BPMS must support seamless integration with third-party applications, without causing any disruption in process execution or loss of data.
Advanced reporting and analytics
The BPMS platform must provide advanced reporting and analytics features that enable process owners to be updated on performance.
Top BPMS Platforms for 2025
Choosing the right Business Process Management Software (BPMS) can make or break your automation strategy in 2025. Whether you’re a small business or an enterprise, these top platforms offer powerful tools to streamline, optimise, and scale your workflows. Here’s a quick look at the leading BPMS platforms for the year ahead:
1. Cflow
Cflow is a no-code, cloud-based BPMS that simplifies workflow automation for growing teams and mid-sized businesses. With an intuitive drag-and-drop interface, it empowers non-technical users to automate processes in minutes. It’s built for flexibility, security, and speed.
Features:
Visual Workflow Builder
Drag-and-Drop Form Designer
AI Copilot and Rule-based Automation
Custom Reports and Approvals
Mobile Access and SLA Tracking
Best For:
Mid-sized businesses looking for cost-effective, no-code process automation across HR, Finance, and IT without developer support.
2. Appian
Appian is an enterprise-grade low-code automation platform known for unifying data, people, and systems in one workflow. It offers both on-premise and cloud deployment options and scales efficiently for complex enterprise needs.
Features:
Low-Code Development
Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
AI and ML Integration
Enterprise Data Fabric
End-to-End Case Management
Best For:
Large enterprises seeking unified automation across legacy systems, with a blend of low-code flexibility and enterprise-level governance.
3. Bizagi
Bizagi stands out with its user-friendly process modelling and automation platform that supports both business and IT collaboration. It offers on-cloud, on-premise, and hybrid options with strong BPMN 2.0 support.
Features:
Process Modeller
Digital Twin Simulation
Integration with ERP & CRM
Workflow Analytics
Process Automation Lifecycle
Best For:
Organisations are looking for powerful process modelling capabilities with BPMN support and hybrid deployment flexibility.
4. Genpact (Cora)
Genpact Cora is a digital business platform designed to transform complex enterprise operations using AI-powered process orchestration. It offers deep domain expertise, particularly in finance, supply chain, and customer service.
Features:
AI/ML Driven Insights
Process Intelligence
Industry-specific Workflows
Human-in-the-loop Automation
Scalable Cloud Platform
Best For:
Enterprises in highly regulated or complex sectors like BFSI, healthcare, or supply chain are looking for domain-led digital transformation.
5. Pegasystems
Pega offers an AI-powered BPM and CRM platform with a strong emphasis on decision-making and case management. Known for dynamic workflows and scalable enterprise solutions, it combines automation with real-time analytics.
Features:
Case Lifecycle Management
AI-based Decisioning Engine
Omnichannel UX Integration
Cloud-native Architecture
Robotic Automation
Best For:
Customer service-intensive industries that need AI-powered case management and smart decision-making at scale.
6. IBM Business Automation Workflow
IBM’s BPM platform integrates workflow automation, content services, and AI to deliver intelligent automation. It helps enterprises build resilient, AI-enhanced workflows that adapt to changing business demands.
Features:
AI-Powered Workflow Automation
Advanced Content & Document Management
Integration with IBM Watson
Real-Time Analytics
Business Rules Engine
Best For:
Enterprises with legacy infrastructure needing deep integration, scalability, and advanced AI capabilities for end-to-end automation.
Challenges of BPMS
Any big transformation comes with risks and challenges, it is the same with BPMS adoption and implementation. The biggest challenge is the reliability of the software. Some of the common BPMS challenges are listed below –
Maintenance and upgrade – Most of the traditional code-driven BPMS platforms are hard to maintain and upgrade. They need in-house talent and extensive training to maintain and decode.
Complex features – BPMS platforms usually come with multiple complex features that users don’t understand and most probably do not use either.
Conclusion
As organisations across the UK scale their operations, the demand for streamlined and optimised processes grows just as quickly. According to a Market Research Report by the iMac Group, the global business process management market, valued at $13.3 billion USD in 2022, is projected to reach $24.5 billion by 2028. Traditional BPM systems often hinder progress with their reliance on complex, code-heavy implementations.
Cloud-based BPM platforms like Cflow eliminate these hurdles by offering intuitive, no-code visual workflow builders. This empowers teams to automate processes without needing technical expertise, making process management faster, smarter, and far more accessible.
Experience the benefits of no-code cloud BPM for your business.
Start your free trial with Cflow today.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the difference between BPM and BPMS?
BPM (Business Process Management) is the discipline or practice of analysing and improving business processes. BPMS (Business Process Management System) is the software or tool used to automate, monitor, and optimise these processes.
2. How do I know if my business needs a BPMS?
If your organisation has repeatable tasks, manual workflows, limited process visibility, or frequent delays and errors—especially in areas like HR, finance, procurement, or compliance—then a BPMS can dramatically improve your efficiency and control.
3. Can a BPMS integrate with my existing software tools?
Yes, most modern BPMS platforms offer third-party integration capabilities with popular tools such as ERPs, CRMs, HRMS platforms, and communication apps, ensuring seamless workflow automation without disrupting your current systems.
4. Is BPMS only for large enterprises?
No. While large enterprises use advanced BPMS platforms, there are no-code and low-code solutions like Cflow designed for small to mid-sized businesses that require minimal technical expertise to set up and manage workflows.
5. What are the key features I should look for in a BPMS?
A good BPMS should offer a visual workflow builder, role-based access controls, automation triggers, performance dashboards, integration support, and robust analytics and reporting features.
6. How long does it take to implement a BPMS?
Implementation time depends on the complexity of your workflows and the platform chosen. No-code platforms like Cflow can be deployed in days, while enterprise-grade systems might take weeks to fully configure and onboard teams.
Related Articles:
- Empower Your Employees Low Low-Code BPM to Enhance Workflow
- iBPM – A Powerful Medley of Big Data, Analytics, and Business Process Management
- Agile BPM: A Comprehensive Guide To Endorse Agile Business Practices
- Top 3 reasons why Zero code BPM is essential for your business
- RPA vs BPM – Understanding the Commonalities and Differences
- Integration-Centric BPM – The Need of the Hour for Progressive Businesses
What should you do next?
Thanks for reading till the end. Here are 3 ways we can help you automate your business:

Do better workflow automation with Cflow
Create workflows with multiple steps, parallel reviewals. auto approvals, public forms, etc. to save time and cost.

Talk to a workflow expert
Get a 30-min. free consultation with our Workflow expert to optimize your daily tasks.

Get smarter with our workflow resources
Explore our workflow automation blogs, ebooks, and other resources to master workflow automation.